3 Surprisingly Efficient Botanical Extracts For Skin Lightening
With the increase in people's demand to return to nature, botanical extracts in cosmetics with fewer side effects and less toxicity [1] are more and more favored by people. Nowadays, the natural plant extracts with more research reports mainly include saponins, alkaloids, polysaccharides, tea polyphenols, flavonoids, volatile oils, etc., and their efficacy components and related mechanisms have been gradually discovered and confirmed. The efficacy of botanical extracts for skin lightening, sunscreen, anti-aging, sterilization, etc., is remarkable. In this article, you will know 3 surprisingly efficient Botanical Extracts for Skin Lightening, guess what are they?

Mechanism of Botanical Extracts for Skin Lightening
The mechanism of skin lighting is to inhibit melanin production during melanogenesis and metabolism, and the mechanism of melanin inhibition can be divided into intracellular inhibition and extracellular inhibition. Intracellular inhibition refers to the inhibition of melanin formation by inhibiting the activity of tyrosinase, the main rate-limiting enzyme in the melanin formation process, or inhibiting the synthesis of tyrosinase, thus inhibiting the formation of melanin. Extracellular inhibition refers to the inhibition of melanin formation through the inhibition of endothelin-1 and endothelin-2. At present, the more widely used plant extract-based whitening ingredients in the cosmetic industry are mainly licorice extract, arbutin, mulberry extract and so on [2].
1. Licorice Extract
Glycyrrhiza glabra extract is prepared by extracting the roots and stems of the plant Glycyrrhiza glabra, and its main components include glycyrrhizin, glycyrrhizinic acid, glycyrrhizin, isoglycyrrhizin, neoglycyrrhizin, neoisoglycyrrhizin, glycyrrhizin, isoglycyrrhizin, as well as glycyrrhizinidin, glycyrrhizinol, isoglycyrrhizinol, 7-methylcoumarin, and umbelliferolactones, among dozens of compounds [3].

Glycyrrhiza glabra extracts have skin-lightening and sunscreen effects, among which glycyrrhizin and photoglycyrrhizidine have significant whitening effects [4], mainly by inhibiting the activity of tyrosinase and dopa pigment interconjugating enzyme (TRP-2), and by hindering the polymerization of 5, 6-dihydroxyindole (DHl) to prevent the formation of melanin, which can lead to the whitening effect of the skin.
The Three Main Principles of Glabridin for Skin Lightening Are as Follows:
(A) Inhibition of Tyrosinase Activity
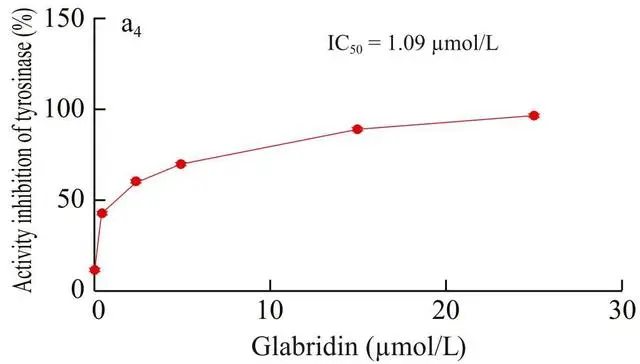
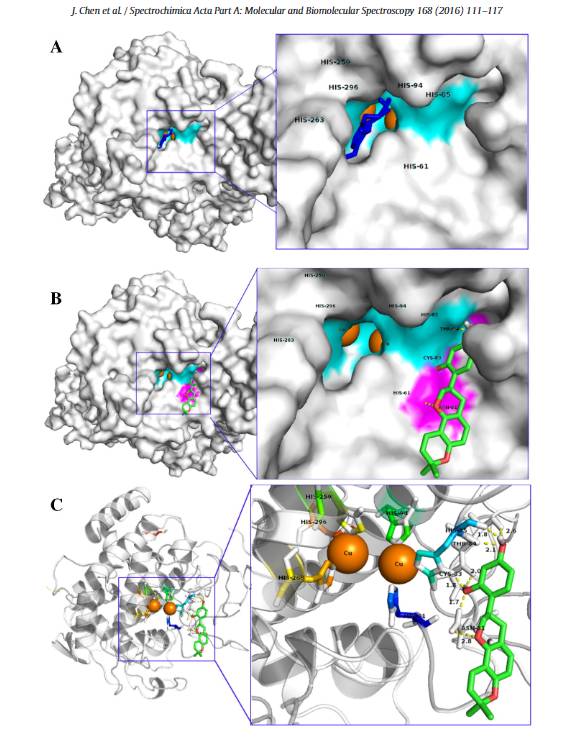
Photoglycopyrrolidine has a very strong inhibitory effect on the activity of tyrosinase with remarkable effect. The results of computer simulation show that photoglycodine can be firmly combined with the active center of tyrosinase in the form of a hydrogen bond, guarding the doorway of tyrosinase, the raw material (tyrosine) for the production of melanin can't enter into the processing plant, and the generation of melanin is inhibited.
(B) Inhibition of Reactive Oxygen Species Production (Antioxidant)
Under UV stimulation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) can be induced to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage the phospholipid membrane of skin tissue and manifest as erythema and pigmentation on the skin. Therefore, reactive oxygen species are a substance that can cause skin pigmentation.
Experimental studies have shown that glyphosate and superoxide dismutase (SOD) have similar ability to scavenge free radicals (i.e., antioxidants). This to some extent weakens the increase in tyrosinase.
(C) Suppression of Inflammation
After the skin tissue is damaged by ultraviolet rays, erythema and hyperpigmentation occur along with inflammation, which further promotes the formation of melanin, resulting in a vicious cycle.
Glabridin has the effect of inhibiting inflammation, to a certain extent, to inhibit the formation of melanin to create favorable conditions, but also can promote the repair of damaged skin [5].
2.Arbutin
Arbutin [6] is the arbutus leaf extract, the main components are arbutin, arbutin, arbutin acid, etc. The arbutin whitening effect is remarkable. Arbutin whitening effect is remarkable, it can quickly penetrate into the skin, without affecting the concentration of skin cell proliferation under the premise, and can effectively inhibit the activity of tyrosinase in the skin in order to block the formation of melanin, it through the combination of itself and tyrosinase, accelerate the decomposition of melanin and excretion, so as to reduce the pigmentation of the skin, to get rid of pigmentation and freckles. At the same time, arbutin does not produce toxicity, irritation, sensitization and other side effects on melanin cells, and also has emollient, healing, sterilization and synergistic anti-inflammatory effects.

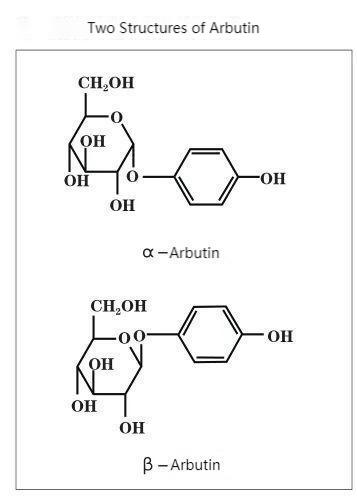
Arbutin can be categorized into α-type and β-type according to its structure. α-Arbutin is chemically known as 4-hydroxyphenyl-α-D-glucopyranoside, and β-arbutin is chemically known as 4-hydroxyphenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside. α-Arbutin is a differential isomer of β-arbutin, and its glycosidic bonds are spatially oriented in the opposite direction to those of β-arbutin (see the figure for details).
Mechanism of Skin Lightening Effect of Arbutin
The content and distribution of melanin is the main factor in determining skin color. Melanin is produced in melanocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis and is formed by tyrosine under the action of tyrosinase through a series of complex biochemical reactions, and is transferred to the outer layer of the epidermis through synapses from the basal layer from the inside out to color the skin.
Tyrosinase has tyrosine hydroxylase activity (catalyzes the production of dopa from tyrosine) and dopa oxidase activity (catalyzes the production of dopaquinone from dopa), and as the main rate-limiting enzyme in the process of melanin formation, its activity determines the amount of melanin formed.
Arbutin, on the other hand, is a tyrosinase inhibitor, which can effectively inhibit tyrosinase activity without affecting the concentration of cell proliferation. Through its own direct binding with tyrosinase, it competes for the binding site of dopa and blocks the synthesis of dopa and dopaquinone, which then interferes with the melanocytes and inhibits the production of melanin. At the same time, it also has the function of lightening the formed melanin, accelerating the decomposition and excretion of melanin, reducing skin pigmentation, and getting rid of pigmented spots and freckles.

In recent years, arbutin has been applied to cosmetic products in many countries to whiten the skin, such as Shiseido, an internationally famous brand in Japan.
3 . Mulberry Leaf Extract
Mulberry leaf extract is derived from its dried leaves, and the main components are chlorogenic acid, reducing sugars,polysaccharides and galacturonic anhydride, tannins, flavonoids, polyphenols and other substances.

Mulberry leaf extract can inhibit tyrosinase activity, reduce the formation of melanin in the skin, and improve the physiological function of the skin, with a whitening effect. It also has an obvious antioxidant effect and scavenging effect on superoxide ion radicals. At the same time, mulberry leaf extract has a strong inhibitory effect on the activity of tyrosinase, which catalyzes the biosynthesis of melanin. The depth of skin color is mainly determined by the amount of melanin, and tyrosinase is the key enzyme in melanin synthesis, and the inhibition of its activity has the effect of delaying the regression of plaques or lightening of pigmentation [7][8].
Reference
[1] Xie Huiying, Chen Baohua, Zhang Jintao. Application of Several Plant Extracts in Cosmetics[J]. Flavor and Fragrance Cosmetics,2012(3):50-53.
[2] Yang Jiameng. Application and Prospect of Plant Extracts in Cosmetics[J]. Daily Use Chemical Industry,2013,43(4):313-316.
[3] Wang Yuqing,Zhu Mei. Investigation and Analysis of Licorice Resources in China[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University,2002(4):366-369.
[4] Zhang Lianxue,Zhang Liming,Wang Juan, et al. Application of Licorice in Cosmetics[J]. Flavor and Fragrance Cosmetics,2010(4):45-48.
[5] Huang Wei. Clinical Study on the Treatment of Chloasma with Licorice Extract Whitening Cream[D]. Hunan:Master's thesis of Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2013.
[6] Fang Jun,Du Shunjing. Research Progress on the Application of Arbutin in Cosmetics[J]. Health Research,2009,38(1):111-113.
[7] Wang Jujun, Lei Yang, Fu Yicai. Current Status of Whitening Research on Extracts of Morus Alba and Progress of Their Application[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2013,40(265):113-118.
[8] Li Ying, Li Qingdian. Study on the Antioxidant Effects of Mulberry Polysaccharides[J]. China Brewing,2010(4):59-61.


 English
English French
French Spanish
Spanish Russian
Russian Korean
Korean Japanese
Japanese





