The Secret Guide To What Is A Botanical Extract
Do you know what is a botanical extract and what is its classification? What are the 8 main production processes for plant extracts? What Are the 6 Main Active Ingredients of Plant Extracts? Please read the secret guide to what is a botanical extract below.
What Is a Botanical Extract?
A botanical extract refers to the product formed by taking plants (including tissues, fruits, etc.) as raw materials and going through the physical and chemical extraction and separation process to obtain and concentrate one or more active ingredients in the plants in a targeted manner, without changing the active ingredient polarity. It can be widely used as raw material in the industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, health care products and cosmetics.
What Are the Classifications of Botanical Extracts?
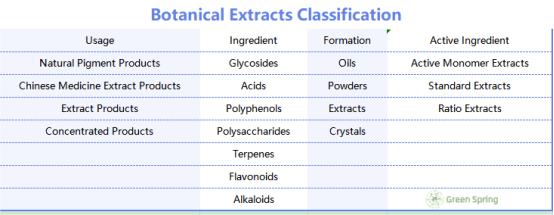
There are many kinds of botanical extracts, and more than 300 kinds of plant extracts have been industrially extracted. There are various ways to categorize them. According to the content of active ingredients, they can be divided into three categories: active monomer extracts, standard extracts and ratio extracts; according to the composition, they can be divided into glycosides, acids, polyphenols, polysaccharides, terpenes, flavonoids, alkaloids and so on; and according to the form of the products, they can be divided into plant oils, extracts, powders, crystals and so on. According to the use, plant extracts can be divided into natural pigment products, Chinese medicine extract products, extract products and concentrated products.
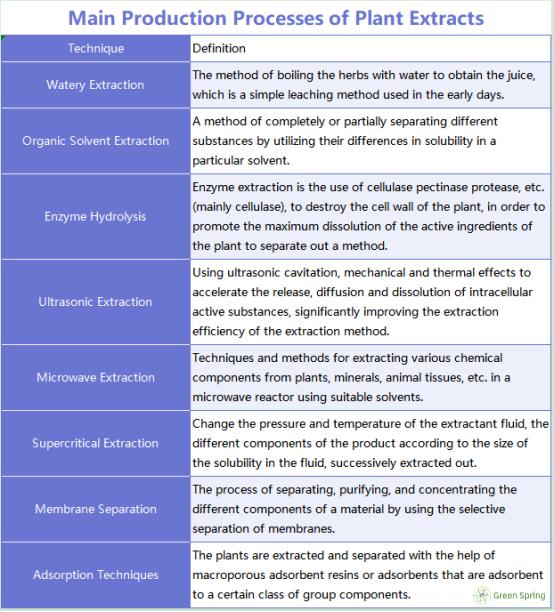
What Are the 8 Main Production Processes for Plant Extracts?
What Are the 6 Main Active Ingredients of Plant Extracts?
1. Alkaloids
Alkaloids, i.e. plant bases, are alkaline nitrogen-containing organic compounds with significant biological activity or toxicity and are the active ingredients of Chinese herbal medicine.
Chemical properties: colorless, bitter taste; mostly alkaline; generally insoluble or insoluble in water and alcohol, soluble in organic solvents; its salts are more polar, and soluble in water and alcohol.
The main plant extracts containing alkaloids: berberine (Berberine 97% HPLC) in Huanglian, ephedrine in Ephedra, lisdexamfetamine in Rohypnol, comedone in Hibiscus, vincristine in periwinkle, morphine and heroin.
2. Flavonoids
Flavonoids are widely found in all parts of plants, especially in flowers and leaves, and about 20% of herbal medicines contain flavonoids, which are rich in resources.
The main effects of flavonoids are antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-mutagenic, antihypertensive, antioxidant, anti heat and detoxification, anti-cancer, anti-cancer, and so on.
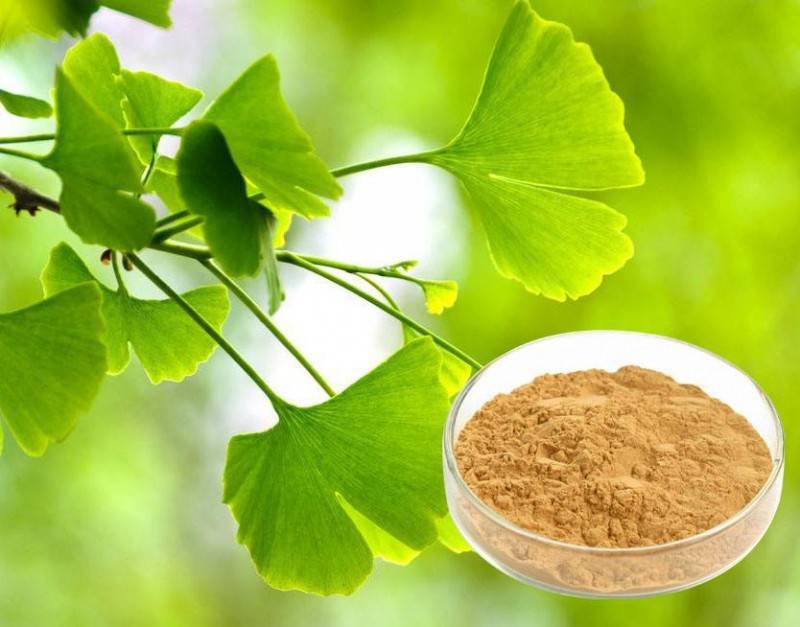
Standard plant extracts containing flavonoids: propolis, soy isoflavones, anthocyanins, green tea extract, and ginkgo biloba extract.
3. Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides, also known as polysaccharides, are made of monosaccharides connected by glycosidic bonds, the basic structural unit is glucan, and their relative molecular mass is generally tens of thousands or even millions.
The main effects of polysaccharide active ingredients: enhance immunity, antioxidant, lowering blood sugar, lowering blood lipids, promoting intestinal health, regulating intestinal flora balance.
Common polysaccharides: edible mushroom polysaccharides, algal polysaccharides, herbal polysaccharides and so on.
4. Glycosides
Glycosides, the active ingredients of plant extracts, combine sugars and phenols or flavonoids.
Chemical properties: colorless and odorless, with a bitter taste, acidic or neutral; can be dissolved in water and ethanol.
Common glycosides: radish glycosides, amygdalin, salicin, cardiac glycosides, saponins and so on.

5. Organic Acids
Organic acid compounds can replace antibiotics, are used in feed as a preservative; can also regulate the intestinal flora.
Common organic acids: chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, tartaric acid and so on.

6. Volatile Oils
Volatile oil extracts with volatile physical properties can be volatile with water vapor distillation, and most volatile oil extracts have a certain aroma, often used as essential oils.
Common volatile oil extracts: peppermint oil, rose oil and so on.

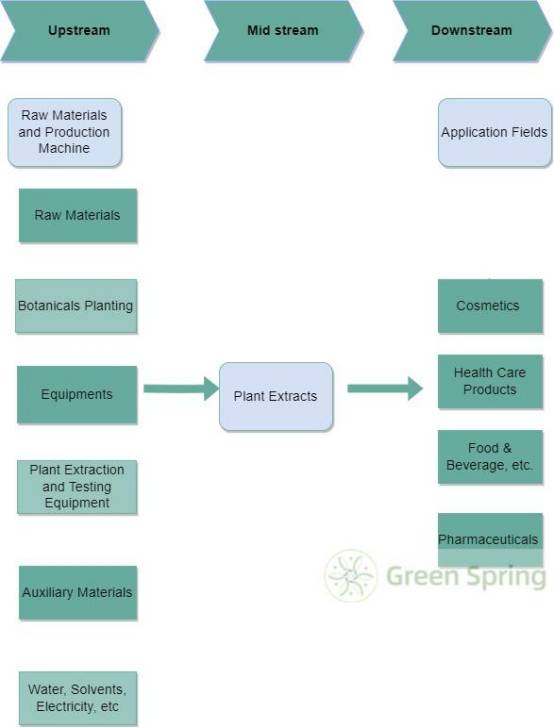
Flow Chart of Botanical Extracts Industry Chain
The upstream of the botanical extract industry chain is raw materials, plant extraction equipment and other auxiliary materials; the midstream is plant extraction and deep processing; and the downstream is food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, health products and cosmetics and other application industries.
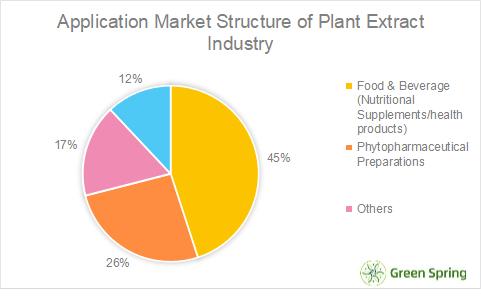
Market Structure of Downstream Applications in the Plant Extraction Industry
From the downstream application market structure chart, the food and beverage industry is the main application area, accounting for nearly 50%, botanical pharmaceutical preparations are second only to food and beverage, accounting for 26%.
What Are the Key Production Origins of Botanical Extracts in China?
Shaanxi, Hunan and Sichuan are China's three main producing areas of plant extracts. The botanical extract industry in these three provinces started early and is relatively rich in medicinal plant resources, and has formed a specific scale advantage.
Shaanxi is one of the birthplaces of botanical extracts in China and is currently the main production area of plant extracts in China, with more than 600 enterprises engaged in producing more than 2,000 varieties. With the scale of continuous growth (15 consecutive years, the average annual increase is about 25%).
Hunan is located in central China, rich in forest resources and with a favorable ecological environment, which gives unique conditions for the growth of Chinese herbal medicines, with a wide variety of Chinese herbal medicines and abundant reserves. According to statistics, there are nearly 2,400 kinds of Chinese herbal medicines in Hunan, accounting for 18.7% of China's total; there are 4.5 million mu of planting bases for Chinese herbal medicines, of which 2.8 million mu are bulk Chinese herbal medicines bases, and the number of key varieties of Chinese herbal medicines in Hunan ranks the second in China.
The output of Chinese herbal medicines such as yuzhu and lily accounts for a considerable share in China. The resource advantages and industrial advantages of Chinese herbal medicines have created excellent conditions for the industrial development of plant extracts with Chinese herbal medicines as the primary raw materials. Hunan's export volume of Chinese herbal medicines and plant extracts ranks top in China, and the development momentum is fast and good. Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Guangxi, Yunnan and the three northeastern provinces are also involved.
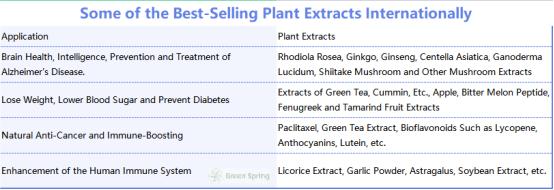
What Are the Best-Selling Plant Extract Internationally?
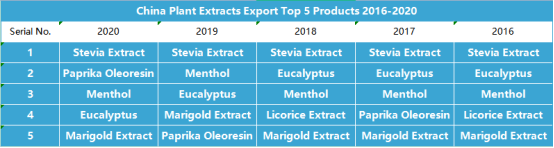
What Are the Top 5 Plant Extracts China Exported from 2016 to 2020?
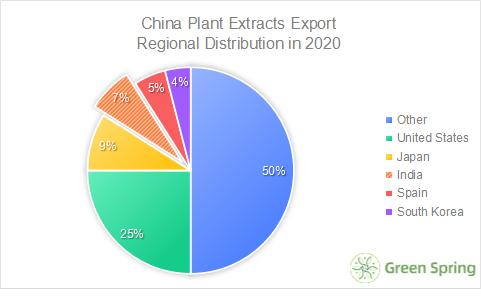
China Plant Extracts Export Regional Distribution in 2020
From the distribution of export regions, North America, Asia and Europe are the main consumer markets of global plant extracts. According to the data statistics of the Chamber of Commerce of Medical Insurance, in 2020, China's plant extract exports ranked the top ten countries and regions, in order of the United States, Japan, India, Spain, South Korea, Mexico, France, Germany, Hong Kong, China, Malaysia, of which the exports to the United States and Japan accounted for a considerable proportion of the total, accounting for 25% and 9% respectively.
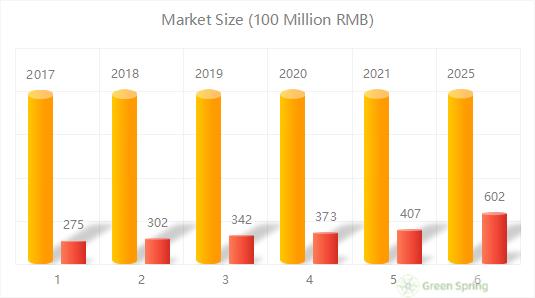
China Plant Extract Industry Market Size 2017-2025
In recent years, the plant extract industry has been growing, with the market size increasing from 27.5 billion RMB in 2017 to 40.7 billion RMB in 2021, and it is predicted that the market size of the botanical extract industry will exceed 60 billion RMB in 2025.
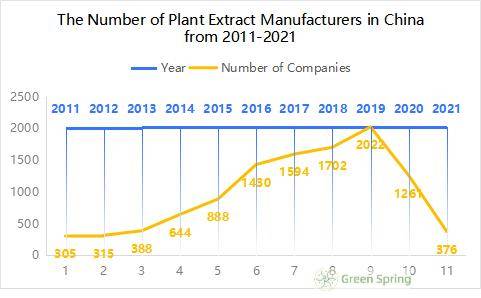
How Many Plant Extract Companies Are There in China?
The number of plant extract manufacturers in China multiplied from 2011-2019, from 305 to 2,022, and fell off a cliff after 2020, with only 376 in 2021. The following chart shows the number of plant extract manufacturers in China from 2011-2021.
What Is the Current Development Status of China's Botanical Extract Industry?
China's botanical extracts began to develop in the 1970s, but at that time, due to the embryonic stage, did not form an independent industry. It was only in the 1990s, with the development of foreign trade, that China's plant extract industry entered the starting period. Subsequently, in the 21st century, the market entered a period of development as new technologies were adopted in large quantities.
Since the 21st century, the number of Chinese botanical extract-related enterprises has been increasing as the market continues to grow. Although the number of registered enterprises declined in 2020 due to the epidemic. However, the number of related enterprises is expected to increase as the epidemic is effectively controlled and market demand picks up.

Data shows that as of November 2021, the number of surviving and active enterprises in China's plant extract production totaled 10,144, with 376 new enterprises from January to November. The enterprises are mainly located in Guangdong, Shaanxi and Hunan, with the number of plant extract-related enterprises in the region amounting to 2,974, 1,412 and 1,338, respectively.
-
Prev
Do You Need A List Of Botanical Extracts Efficient For Skin Aging?
-
Next
What Are Botanical Extracts Benefits in Feed?


 English
English French
French Spanish
Spanish Russian
Russian Korean
Korean Japanese
Japanese







