What Is Black Rice Anthocyanin?
Anthocyanin is a natural flavonoid polyphenol compound formed by the combination of anthocyanidins and various glycosides in a natural state with a 2-phenylbenzopyran cation structure as the backbone. It is a product of secondary plant metabolism, widely distributed in the cell sap of the flowers, fruits, roots, stems and leaves of plants. It is the main source of the gorgeous colors in nature. have physiological activities such as scavenging free radicals in the body, anti-tumor, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, inhibiting lipid peroxidation, inhibiting platelet aggregation, preventing diabetes, weight loss and protecting eyesight.
Black rice Anthocyanin is an important class of anthocyanin substances. With people's growing awareness of self-care, the nutritional value of black rice, especially its functional ingredient anthocyanin and its pharmacological effects, has aroused great interest among researchers, producers and consumers. This paper therefore analyzes the structure and composition of black rice anthocyanins, reviews the latest research results on black rice anthocyanins in terms of their antioxidant, liver protection, anti-lipid, anti-cancer and weight loss properties, and comments on future trends in the research and application of black rice anthocyanins, with a view to better exploiting and developing this precious specialty rice resource for human nutrition and health.
1 Structure and composition of black rice anthocyanins
1. 1 Structure of black rice anthocyanin
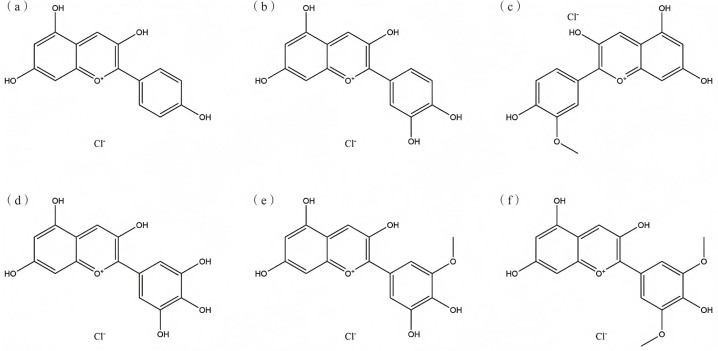
The structure of black rice anthocyanin is similar to that of other anthocyanins. The carbon skeleton of the parent nucleus is composed of a 2-phenylbenzopyran cation. Anthocyanins are soluble in polar solvents such as water, methanol, and ethanol, and are easily affected by factors such as light, temperature, and pH, which can cause structural changes. Studies have found that as factors such as pH change, the structure of black rice anthocyanin changes, and the position of its characteristic absorption peak shifts red or blue accordingly [1]. In plant tissues, black rice anthocyanins mainly exist in the form of glycosides, with a very small proportion existing in the form of aglycones. The number of sugar groups is generally 1 to 3, and they are usually located at the 3, 5, and 7 positions of the A and C rings of the parent nucleus and at the 3' and 5' positions of the B ring. The linked sugar groups are mainly D-glucose, L-rhamnose, and D-galactose.
1. 2 Black rice Anthocyanin component preparation analysis research
At present, the main components of black rice anthocyanins reported in the literature are 3,5-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-2-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one-3-glucoside,3-glucoside, 3-rhamnoside,3,5-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-2-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one-3-glucoside, paeoniflorin-3-glucoside, paeoniflorin-3-arabinoside, and malvin-3-galactoside, etc. 8 species [2]. Due to differences in extraction purpose, extraction material, extraction method, purification technology, testing equipment, etc., the anthocyanin content of black rice sold in the market also varies. A study used a VARIAN Prostar 210 HPLC-type preparative liquid chromatograph to prepare and analyze black rice produced in Hanzhong. The results showed that eight black rice anthocyanin components were obtained based on the order of the anthocyanin component peak times. At the same time, liquid-mass spectrometry was used to analyze and detect the eight component samples, obtained 14 possible Anthocyanin components of the relevant technical parameters [3], the method of black rice Anthocyanin components of further analysis, the preparation of standards and structural identification work has important reference significance.
2 Black rice Anthocyanin pharmacological effects
2. 1 antioxidant effect
Free radicals are highly oxidizing and can damage the body's tissues and cells, which in turn can cause cancer, aging and other chronic diseases. The human body constantly produces free radicals due to respiration and external environmental factors. Anthocyanin compounds are a type of important natural antioxidant that can effectively remove the damage caused to the human body by free radicals. Wang Qiao'e et al. used a solvent extraction method to separate the crude anthocyanin extract of black rice into four fractions with different polarities. The results of their study on the antioxidant strength of the fractions with different polarities showed that the water-soluble fraction of black rice anthocyanin had the strongest ability to scavenge 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl free radicals and hydroxyl free radicals; Further column chromatography was used to subdivide the water-soluble components into five components (C1 to C5), and the activity of each component in scavenging DPPH free radicals and hydroxyl free radicals was analyzed. The antioxidant capacity of each component, from largest to smallest, is as follows: C2 > C3 > C4 > C1 > C5 [4].
Liang Yinku et al. studied the inhibition of hydroxyl radicals and superoxide anions by black rice anthocyanins and their total antioxidant activity, and concluded that black rice anthocyanins can effectively scavenge free radicals, have a good antioxidant effect, and that the inhibition of hydroxyl radicals and superoxide anions and their total antioxidant activity increase with the increase of sample concentration [5]. Liu Qin et al. used the FRAP, DPPH and ORAC methods to determine the antioxidant activity of black rice anthocyanin. The results showed that in the FRAP and DPPH methods, the antioxidant activity of black rice anthocyanin was higher than that of purple cabbage anthocyanin, which was consistent with the structure-activity relationship of anthocyanin, while the results of the ORAC method were the opposite [6].
Li Jingjing found that black rice anthocyanin can significantly improve the total antioxidant capacity of mouse serum and liver, inhibit the ability of hydroxyl free radicals and the total superoxide dismutase level, and reduce the content of malondialdehyde. The antioxidant effect is in a dose-dependent manner with its concentration [7]. Shi Juan et al. also showed that black rice anthocyanin has an antioxidant effect in mice [8]. From the above research results, it can be seen that black rice anthocyanin has antioxidant properties, and its antioxidant capacity is closely related to the structure, composition and concentration of black rice anthocyanin [9-10]. The mechanism of antioxidant action lies in the fact that its phenolic hydroxyl groups provide hydrogen atoms, prevent the oxidation of body fat, enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes, reduce the content of lipid peroxides and lower the level of oxidative stress [11]. Clinically, the appropriate introduction of exogenous antioxidants, such as the safe and non-toxic black rice anthocyanin, can remove free radicals from the human body, slowing or improving diseases caused by free radicals. At present, the research on the antioxidant properties of black rice anthocyanin is still in the stage of in vitro and in vivo antioxidant tests.

2. 2 Hepatoprotective effect
The liver is responsible for important physiological functions in the human body, so it is of great practical significance to screen for drugs, health foods or foods that protect the liver. It has been found that black rice anthocyanins have a certain effect on the prevention and treatment of liver damage. Hou Fangli studied the protective effect of black rice anthocyanins on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver damage in mice. The results showed that black rice anthocyanins can improve liver cell damage, significantly increase the survival rate of liver cells, and the higher the concentration, the better the effect, and there is a clear dose-effect relationship.
The mechanism may be that black rice anthocyanin can significantly reduce the activity of liver enzymes in mice with CCl4 liver damage and reduce pathological damage to the liver tissue [11]. Lu Hongchao et al. studied the protective effect of black rice anthocyanin compound capsules on experimental liver injury. The results showed that black rice anthocyanin compound capsules can significantly increase SOD activity in liver tissue, improve liver fibrosis, and have a certain preventive effect on CCl4 liver injury. Further studies have found that black rice anthocyanin compound capsules also have a certain effect on alcoholic liver injury [12-13]. In addition, Hao Jie found that black rice anthocyanin has a protective effect on the oxidative stress-induced nephrotoxicity of potassium bromate (KBrO3) and the stress-induced hepatotoxicity induced by restraint [14].
2. 3 Anti-lipid effect
Hyperlipidemia is a disease caused by factors such as genetic defects, improper diet, and metabolic disorders, in which plasma lipids are higher than normal. Disorders of lipid metabolism or abnormal lipid metabolism are considered to be one of the important pathogenesis of hyperlipidemia. Due to its high risk and high treatment costs, it has become a hot issue of global concern. Many scholars have found that black rice anthocyanins have the effect of regulating blood lipids. Xu Huilong observed the changes in body weight, serum TC and TG levels in hyperlipidemic rats by gavage with black rice husk, red rice husk, red mushroom, ganoderma lucidum and bamboo fungus, with simvastatin as a positive control. After 8 weeks of experimentation, it was found that black rice husk had the most significant overall modulation effect on the blood lipid levels of rats, and was positively correlated with the dose [15]. Zhang Mingwei et al. found that after high-fat rats consumed black rice anthocyanins, the activity of antioxidant enzymes in the serum and liver increased significantly, and the blood lipid levels and atherosclerosis index were significantly lower than those in the high-fat model group. Anthocyanin compounds and unsaturated fatty acids may be the main substances responsible for these effects [16].
Zhuo Xueming studied the anti-hyperlipidemic effect of black rice anthocyanins by feeding anthocyanins and black rice bran to hyperlipidemic and hyperglycemic model mice. The results showed that black rice anthocyanins have the effect of regulating blood lipids and blood sugar [17]. Yao Shulong established an in vitro pancreatic lipase model, a bile acid micelle model and a Caco-2 cell model to investigate the effects of black rice anthocyanins on pancreatic lipase activity, the solubility of cholesterol in micelles and the uptake of cholesterol by small intestinal cells. The results showed that black rice anthocyanins have the effect of inhibiting pancreatic lipase activity, reducing the solubility of cholesterol in micelles, reducing the uptake of cholesterol by small intestinal cells, regulating blood lipids, and preventing hypercholesterolemia. In addition, the inhibitory activity is positively correlated with the anthocyanin content.
Guo Honghui et al. observed the effect of black rice anthocyanin on insulin in rats fed a high-fructose diet by adding black rice anthocyanin to a high-fructose diet. The results showed that black rice anthocyanin has a preventive and ameliorative effect on insulin in rats caused by a high-fructose diet, can inhibit the activation of aminopeptidase in adipose tissue, significantly increased insulin receptor substrate tyrosine phosphorylation and glucose transporter translocation after insulin stimulation. The mechanism may be that black rice anthocyanin improves insulin sensitivity in fructose-fed rats by inhibiting the activation of aminopeptidase [19].

2. 4 Anti-cancer and anti-tumor effects
In recent years, the anti-cancer and anti-tumor effects of black rice anthocyanins have attracted increasing attention. Luo Liping's research shows that black rice anthocyanins can inhibit the growth and proliferation of breast cancer cells and promote apoptosis of cancer cells. The mechanism may be that anthocyanins competitively bind to the HER-2 receptor with ATP, regulate its phosphorylation level, reduce the activity of pro-metastasis enzymes, and weaken the metastatic ability of breast cancer cells [20]. Weiwei Jiang found that black rice extract can inhibit the proliferation of human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. The mechanism may be through the phosphorylation of p38 and JNK and upregulation of NO and ROS levels, leading to cell mitochondrial damage, cytochrome C release and other pathways to induce apoptosis [21].
Li Jingjing found that the highest tumor inhibition rate of black rice anthocyanin extract on S180 tumor-bearing mice reached 32.17%, and the tumor inhibition rate was positively correlated with the dose. Black rice anthocyanin extract can significantly increase the thymus index and spleen index of S180 tumor-bearing mice. The highest thymus index in each dose group reached 2.162 mg/g, and the spleen index reached 5.298 mg/g, which were 28% and 35% higher than the cyclophosphamide control group, respectively, indicating that black rice anthocyanins can significantly improve the immune function of S180 tumor-bearing mice [7]. Chang Hui et al. studied the effect of black rice anthocyanins on the proliferation of the HL-60 leukemia cell line. The results showed that black rice anthocyanins have a significant inhibitory effect on HL-60 cell proliferation, can effectively induce HL-60 cell apoptosis, and cause G0/G1 phase arrest [22].
2. 5 Weight loss effect
Obesity is a chronic metabolic disease that is harmful to health and has become a global health problem. Currently, the treatment of obesity has defects such as high cost, easy rebound, and significant toxic and side effects. Therefore, it is important to develop a safe, low-cost, and effective weight loss method. Hu Yan et al. studied the effect of black rice anthocyanin on obesity induced by a high-fat diet in rats. The results showed that black rice anthocyanin significantly inhibited the weight gain induced by a high-fat diet in rats after 12 weeks of feeding, and improved the obesity-related indicators of rats [23].
Wu Tao explored the intervention effect of mulberry fruit, cherry, blueberry and blueberry anthocyanin on high-fat diet-induced obese mice, and found that anthocyanin can only inhibit the weight gain of mice, but cannot change the trend of weight gain in obese mice. Further studies have found that anthocyanin can reduce the accumulation of lipids in serum and liver. Jiao Yan et al. studied the effect of Anthocyanin on lipid metabolism and antioxidant capacity in rats induced by a high-fat diet by gavage with Anthocyanin from the fruit residue of blue indigo berries. The results showed that after 28 consecutive days, Anthocyanin from the fruit residue of blue indigo berries could significantly reduce the blood lipid level of obese model rats, significantly enhance the activity of liver enzymes, and significantly reduce the production of lipid peroxides. can effectively reduce liver peroxidation damage and prevent the occurrence of atherosclerosis [25].
2. 6 Other pharmacological effects
In addition, studies have found that black rice anthocyanins have a variety of pharmacological effects, such as protecting eyesight, promoting the stability of late-stage plaques in mice, enhancing immunity, and protecting the cardiovascular system. Chen Wei et al. found that light can induce apoptosis of retinal photoreceptor cells in rats, and that oral administration of black rice anthocyanins can reduce light-induced apoptosis of retinal photoreceptor cells in rats [26]. Jin Liqin et al. found that black rice anthocyanin has an important regulatory effect on the immune function of rat tissues and organs, and also has a certain antioxidant effect [27]. Yu Xiaoping et al. found that black rice anthocyanin can promote the stability of advanced plaques in mice with apolipoprotein E gene defects, and this effect may be related to its improvement of lipid metabolism [28]. Zhang Mingwei et al. studied the protective effect of black rice anthocyanins on vascular endothelial cell oxidative damage caused by ox-LDL by observing the cell morphology of the EVC304 cell line treated with ox-LDL peroxidation under the protective effect of black rice anthocyanin preincubation. The results showed that black rice anthocyanin can reduce the inhibitory effect of ox-LDL on cell proliferation and significantly reduce the damage to the morphology of endothelial cells caused by ox-LDL [29].
3 Prospects
There are still many problems with the research on black rice anthocyanin. First, the traditional extraction, separation and purification of black rice anthocyanin takes a long time, is costly, has a low yield and high waste water treatment costs; second, due to the difficulty and high cost of purification and preparation of black rice anthocyanin standards, the price of standards is expensive, and equipment requirements are high, which in turn causes difficulties in structural analysis and identification of black rice anthocyanins, and it is difficult to obtain a single component of anthocyanins; third, black rice anthocyanins have the effects of anti-oxidation, liver protection, anti-lipid, anti-tumor, immune regulation, weight loss, etc., However, there have been more in vitro environmental simulation studies on the physiological effects of black rice, and relatively few animal experiments and clinical application studies, especially in the structure-activity relationship of black rice anthocyanins, the quantitative-activity relationship and the molecular and physiological mechanisms of their effects, which still require further in-depth research. Fourth, the anthocyanin content in black rice is relatively low. Further research is still needed on how to use bioengineering and agricultural techniques to screen for black rice varieties with high anthocyanin content and to improve the anthocyanin content of black rice.
Currently, there are many health products on the market related to black rice, such as black rice wine, black rice vinegar, black rice health tea, black rice vermicelli, etc., but black rice anthocyanin products are still rare in the domestic market. At present, a group of anthocyanin products represented by black rice anthocyanin capsules are in research and development and trial production. With the development and hot sales of black rice and its anthocyanin health food, the market prospects for black rice anthocyanin will be very broad. Further research into the industrialized automated preparation and separation and purification of black rice anthocyanin, the relationship between the structure of black rice anthocyanin and its biological activity, clinical trials of the pharmacological effects of black rice anthocyanin, and the research and development of related products will remain important areas of focus in the future.
References:
[1] Wang Feng, Deng Jiehong, Tan Xinghe, et al. Research progress on anthocyanin and its co-color effect [J]. Food Science, 2008, 29(2): 472-476.
[2] Wang Yanlong, Shi Shaofu, Han Hao, et al. Research status and prospects of anthocyanin in Chinese black rice.
Chinese Journal of Biochemical Drugs, 2010, 31(1): 63-66. [3] Wang Yanlong. Research on the extraction of black rice anthocyanin and its stability in alcoholic solutions [D]. Shaanxi Institute of Technology, 2010.
[4] Wang Qiao'e, Xie Dan, Qian Jie, et al. Separation and purification of black rice anthocyanins and their antioxidant properties [J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2015 (2): 157-160, 172.
[5] Liang Yinku, Wang Qi, Li Xinsheng. Study on the scavenging of free radicals and antioxidant effects of black rice anthocyanin capsules in vitro [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2012 (8): 243-246.
[6] Liu Qin, Li Min, Hu Qiuhui. Comparative study on the composition, antioxidant properties and stability of black rice bran and purple cabbage anthocyanin extracts [J]. Food Science, 2012(19): 113-118.
[7] Li Jingjing. Genotypic differences in the antioxidant effects of black rice and inhibition of animal tumors [D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2010.
[8] Wang Jinting, Yang Minyi. Relationship between the chemical structure of black rice pigments and antioxidant activity [J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Arts and Sciences (Natural Science Edition), 2007 (6): 59-61.
[9] Shi Juan, Zhang Manli, Sun Hanju, et al. In vivo antioxidant research on black rice anthocyanins [J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2015 (5): 348-351, 369.
[10] Zhang Mingwei. Active ingredients and mechanisms of black rice's antioxidant and hypolipidemic activities [D]. Guangzhou: South China Normal University, 2003.
[11] Hou Fangli. Protective effect of black rice anthocyanins on CCl4-induced liver injury in mice and its antioxidant mechanism [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2009.
[12] Lu Hongchao, Wang Yangke, Li Lixia, et al. Protective effect of black rice anthocyanin compound capsules on experimental liver injury [J]. Food Science, 2013 (3): 261-263.
[13] Lu Hongchao, Wang Qi, Zhang Tao, et al. The preventive and therapeutic effects of black rice anthocyanin compound capsules on alcoholic liver injury.
[14] Hao J. Study on the anti-stress hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic effects of black rice anthocyanins and the composition of black tiger fruit anthocyanins [D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2014.
[15] Xu H. Study on the effects of black rice bran on lipid metabolism in rats and its molecular mechanism [D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2013.
[16] Zhang Mingwei, Zhang Ruifen, Guo Baojiang, et al. Antioxidant and hypolipidemic effects of black rice bran extract and analysis of its components. Chinese Agricultural Science, 2006 (11): 2368-2373.
[17] Zhuo Xueming. Study on the genotype difference of anthocyanin components in black rice and their effect on regulating blood lipids and blood sugar [D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2012.
[18] Yao Shulong. Study on the effect and mechanism of anthocyanin components in black rice on cholesterol absorption [D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2014.
[19] Guo Honghui, Hu Yan, Liu Chi, et al. Effects of black rice anthocyanins on insulin sensitivity in fructose-fed rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 2008(10): 1200-1202.
[20] Luo Liping. Anti-HER-2 positive breast cancer cell metastasis and molecular mechanism study of black rice anthocyanins [D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013.
[21] Jiang Weiwei. Study on the effect and mechanism of black rice hull extract on PC-3 cell proliferation [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010.
[22] Chang Hui, Mi Mantian, Ling Wenhua. The effect of black rice anthocyanins and combined chemotherapeutic drugs on the proliferation of different tumor cells [J]. Journal of the Third Military Medical University, 2007(20): 1943-1946.
[23] Hu Yan, Guo Honghui, Wang Qing, et al. Effect of black rice anthocyanin extract on the formation of obesity induced by high-fat diet in rats [J]. Food Science, 2008 (2): 376-379.
[24] Wu Tao. Intervention of anthocyanins on obesity and its related mechanism [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014.
[25] Jiao Yan, Wang Zhenyu. Effect of anthocyanins from blue indigo fruit on lipid metabolism and antioxidant capacity in rats induced by high-fat diet [J]. Food Science, 2010 (3) :230-234.
[26]Chen Wei, Jia Hao, Yu Xiaoping, et al. The effect of black rice anthocyanins on photochemical injury to retinal photoreceptor cells and Caspase-1 expression in rats [J]. Journal of Chengdu Medical College, 2011 (3) : 196 -199.
[27] Jin Liqin, Liu Mingda, Lv Jianxin, et al. Effects of anthocyanins from black rice on the function of tissues and organs in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemical Drugs, 2012 (1): 16-19.
[28] Yu Xiaoping, Xia Xiaodong, Xia Min, et al. Effects of anthocyanins from black rice husk on the stability of atherosclerotic plaques [J]. Chinese Public Health, 2006(2) : 155 - 156.
[29]Zhang Mingwei, Zhang Ruifen, Guo Baojiang, et al. Protective effect of black rice anthocyanins on peroxidative damage to vascular endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Nutrition, 2006 (3) : 216-220.


 English
English French
French Spanish
Spanish Russian
Russian Korean
Korean Japanese
Japanese






