What Are the Benefits of Blue Berries in Telugu?
Blueberry refers to a blue berry belonging to the genus Vaccinium. There are currently two types: one is a low shrub, a dwarf wild variety with smaller fruits but higher anthocyanin content; the other is a cultivated blueberry, which can grow up to 240 cm tall, with larger fruits that are higher in water content and lower in anthocyanin content. Both perennial shrubs and small berries are fruit trees that are found all over the world, but mainly in areas with a cool climate, plenty of sunshine and slightly acidic soil.
In China, they are mainly distributed in the provinces of Liaoning, Heilongjiang and Jilin. Blueberries have a white powdery surface, delicate flesh, and a moderate sweet and sour taste. They are rich in conventional nutrients such as protein and vitamins, and also contain a considerable amount of minerals and trace elements. They also contain special nutrients such as anthocyanins, phenolic acids, superoxide dismutase and pectin, and are therefore known as the “Queen of Fruits”. In recent years, research into blueberries has been widely applied in China. Therefore, summarizing the main functional components, pharmacological effects and applications of blueberries in the medical, food, cosmetics and other industries is of great significance for promoting the further development and utilization of blueberries.
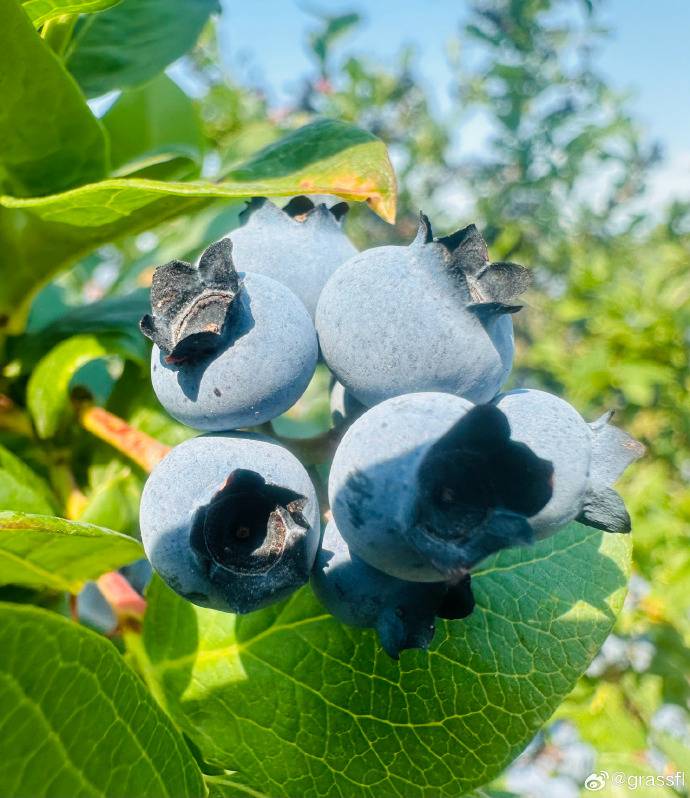

1 Main functional components of blueberries
1.1 Anthocyanins and anthocyanins
In Telugu, Blueberries are a fruit rich in natural dark blue pigments, which are often referred to as anthocyanins or anthocyanidins. Blueberries are rich in anthocyanins and contain a wide variety of these pigments. Anthocyanins are a group of compounds that are formed by the combination of a group of pigments and sugars via glycosidic bonds. They are a class of substances that can appear red based on a flavonoid nucleus. Anthocyanins are derivatives of flavones and flavanones [1]. Blueberries contain five anthocyanins, which can be combined with galactose, glucose and arabinose via glycosidic bonds to form 15 anthocyanins in blueberries. At the same time, they can be converted back into five anthocyanins under the action of acid hydrolysis [2]. Anthocyanins are the main chemical components of blueberry fruit, and the highest content is found in the blueberry peel. The anthocyanin content of blueberries from different regions and varieties varies, but it is generally quite high. Blueberry anthocyanins are natural polyphenolic compounds that are water-soluble small molecules and are easily absorbed and utilized by the body when taken orally.
1.2 Phenolic acids
Blueberries contain a variety of polyphenols, one of which is phenolic acids. Phenolic acids are a type of phenol. The phenolic acid content of blueberries is higher than that of other fruits, but it is greatly affected by the environment and variety. The content is highest in the leaves, and it has good nutritional functions and antioxidant activity. There are more than ten types of phenolic acids in blueberries, of which chlorogenic acid has the highest content. It has a significant inhibitory effect on lung cancer, esophageal cancer, etc., and also has strong antioxidant activity [3]. Organic acids in blueberries account for more than half of the total acids, most of which are citric acid. Ursolic acid, also known as ursoic acid, is a functional ingredient in many natural products with a wide range of biological activities. It plays an important role in anti-tumor.
1.3 Vitamins and minerals
Blueberries contain more vitamins than other fruits and also have a high content of trace elements. They are a type of fruit that is high in amino acids, zinc and iron. Vitamin C is an antioxidant vitamin that maintains the normal function of bones, teeth and blood vessels, and increases resistance. Blueberries have higher vitamin C content than fruits such as mulberries, apples and peaches, and are 20 times higher than cherries. Regular consumption can enhance disease resistance and delay aging. In addition to vitamin C, blueberries are also rich in vitamin E, vitamin A, vitamin B, superoxide dismutase, arbutin, protein, fiber and other minerals, such as K, Fe, Zn, Ca, etc.[4].
2. Pharmacological effects of blueberries
Blueberries are very nutritious. Their flesh is rich in vitamins, protein, dietary fiber, minerals and other nutrients, and the content of these nutrients is higher than that of other fruits. They have certain medicinal functions.
2.1 Protecting eyesight
The eye-protecting effect of blueberries was discovered and recorded in ancient China. Li Shizhen, a famous Chinese medical scientist, discovered a blue berry while collecting medicinal herbs. After taking it, his eyes became moist and clear. He recorded this in the Compendium of Materia Medica, which has been passed down to the present day.
Blueberries contain a lot of anthocyanins, which can clean the capillaries around the eyes and have a good protective effect on the eyes. The anthocyanins contained can increase the moisture and nutrients in the capillaries around the eyes, relieving dry eyes; they can also remove black deposits in the capillaries and improve dark circles under the eyes. It can also relieve eye fatigue, improve night vision, promote the synthesis and regeneration of rhodopsin in retinal cells, prevent myopia, and improve eyesight. It can also effectively prevent the oxidation of the protein in the eye lens and the clouding of the lens, and prevent the formation of cataracts. Long-term consumption can improve night vision and enhance the eye's ability to adapt to low-light environments. During World War II, the US military supplied blueberry jam exclusively to air combat units, which improved the eyesight of air force pilots. Blueberries have since gradually become an indispensable fruit in the daily diet of pilots. In Prevention, the most influential health magazine in the United States, blueberries are called “miracle fruit”.
2.2 Prevention of cardiovascular disease
Anthocyanins in blueberries can regulate the contraction of blood vessels in the body, thereby maintaining blood pressure stability. They can also effectively improve the circulatory system, strengthen capillaries, reduce the stickiness of platelets in the blood, prevent the formation of blood clots, and reduce the incidence of cardiovascular disease [5]. It also has the effect of lowering blood lipids and reducing the occurrence of arteriosclerosis. Anthocyanins can penetrate from the capillaries into the blood, inhibit the permeability of the capillaries, strengthen the capillaries and prevent damage to the capillaries, thereby protecting the brain nerves and preventing Alzheimer's disease.
Blueberries contain a lot of pectin, and apples and bananas contain less than a third of that. Pectin can prevent atherosclerosis and reduce the risk of cardiovascular and other diseases. It can also remove undigested or other toxic substances from the human body, and is beneficial for regulating post-meal blood sugar levels and the balance of intestinal microflora.
2. 3 Anti-cancer
Anthocyanins in blueberries can inhibit the proliferation and spread of cancer cells by regulating related proteins and genes, and prevent cancer cells from damaging and affecting human proteins. They also have the potential to prevent cancer and effectively resist the invasion of cancer cells. Ursolic acid in blueberry fruit has a significant stabilizing and cooling effect on the central nervous system, as well as an anti-cancer effect. In countries such as Japan and the United States, blueberries are ranked first among anti-cancer foods. Regular consumption of blueberries can improve immunity, enhance physical fitness, prevent the occurrence of tissue inflammation, purify cancer-causing factors in the body, and better prevent diseases such as cancer.
2. 4 Antioxidant and anti-aging
The anthocyanins in blueberries have antioxidant properties, can resist free radicals, delay aging, and prevent cell degeneration. Blueberries contain a large amount of anthocyanins, which are dozens of times more effective than vitamin C and vitamin E at scavenging free radicals. They can delay aging and prevent degenerative changes in cells[6], improve the body's immune system, eliminate various inflammations in the body, and reduce the rate of skin and body aging. Collagen and anthocyanins in the human body have a strong affinity for each other, forming a protective film that effectively prevents tissues and cells from being oxidized by free radicals. At the same time, anthocyanins can promote the absorption of vitamin C and vitamin V in the body, enhance the antioxidant and anti-aging effects of blueberries, delay the formation of skin wrinkles, and reduce the damage to the skin caused by ultraviolet rays.
2. 5 Other effects
Blueberries, which are rich in polyphenols, can break down abdominal fat and help control weight. The flavonoids in blueberries can reduce memory loss in the elderly, and eating dried blueberries can improve brain vitality. The anthocyanins contained in blueberries can help stabilize blood sugar in diabetics, improve the sensitivity of insulin to blood sugar, and speed up the metabolism of blood sugar in the body. They are also effective in preventing colon cancer. Blueberries are rich in many trace elements and play a key role in bone development. The folic acid in blueberries can prevent uterine cancer and help the growth and development of the fetus during pregnancy. Blueberries can also treat the common cold, sore throat and diarrhea in children, and they also have a good protective effect on the liver and kidneys.
In recent years, with the accelerated pace of life and increased work pressure, the body's biological clock is prone to disruption, which in turn reduces people's immunity, damages the myelin of the nerves and causes them to harden, reduces the activity of antioxidant enzymes, causes changes in the brain nerves, and leads to a decrease in sleep quality. Anthocyanins in blueberries can protect brain nerves from oxidation, stabilize brain tissue function, and protect the brain from harmful chemicals.
3 Development and application of blueberries
3.1 Medical
The effectiveness of eye disease drugs or health products made from blueberry powdered extracts is generally recognized. Blueberry health capsules have the effect of improving amblyopia and night blindness, relieving eye fatigue, preventing thrombosis, atherosclerosis, protecting capillaries, fighting cancer, and killing bacteria[8]. For example, the Japanese pharmaceutical company has developed health supplements such as “Yao Wang Lanmei Bao” and blueberry eye protection capsules, which are used to treat pseudo-myopia and relieve eye fatigue, and are very popular with office workers who use computers for long periods of time.
France has used anthocyanins and beta-carotene extracted from blueberries to make “Dexamethasone”, has good efficacy in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy and has achieved considerable sales worldwide. In recent years, a number of biotechnology companies in China have teamed up with major hospitals to develop drugs for the treatment of pseudo-myopia and eye fatigue using anthocyanins extracted from rare wild blueberries imported from abroad or from the Greater Khingan Mountains in China. A Shanghai-based eye health chain founded in 2001 has successfully incorporated blueberries into ophthalmic treatments, developing a number of products such as Blueberry Eye Comfort and Blueberry Eye Brightening Su Su. It is constantly discovering the effective ingredients in blueberries, which is more conducive to the application of blueberries in the treatment of eye diseases.
According to big data from the United States, about 12,000 women are diagnosed with cervical cancer each year in the United States. Currently, the most common means of cancer control worldwide is radiotherapy, but radiotherapy can damage nearby healthy cells while destroying cancer cells. Researchers at the University of Missouri School of Medicine found that combining blueberry extract with radiotherapy can increase the effect of radiotherapy through in vitro studies of human cancer cells. Blueberry extract not only inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells, but also induces cancer cell death, effectively inhibiting the production of cancer cells and promoting cancer cell death. This research is of great significance and should be further studied in the future to clarify whether blueberry extract is helpful in the treatment of other types of cancer.
3. 2 Food
In recent years, people have been advocating healthy eating, and in China, blueberries have gradually gained attention as an emerging fruit. Experts and scholars are also continuously deepening their research on the pharmacological effects of blueberries. There are also endless varieties of blueberry derivatives on the market, and sales and prices have increased significantly. Blueberries can be eaten raw or made into dried fruit, preserves, jam, soft candy, etc., and can also be made into tea, suitable for all kinds of people. Blueberry drinks mainly include fruit juice drinks, fruit pulp drinks, compound fruit vinegar drinks, blueberry fruit beer, blueberry wine, blueberry compound fruit wine, blueberry milk drinks, etc.
Because they retain most of the nutrients in blueberries, they are ideal health drinks[7]. Blueberry milk drinks are also popular because they are sweet and sour and have a rich flavor. At present, research on blueberry dairy products in China mainly focuses on product development, while foreign countries pay more attention to the changes in substances during the product processing.

During the production process, some nutrients in the raw blueberries may be destroyed due to external forces such as high temperatures and oxidation. In addition, in order to avoid some problems during transportation, the content of raw blueberries in blueberry products is intentionally reduced, and the content of auxiliary ingredients is increased. Overall, research on blueberry drinks has focused on analyzing changes in active substances during processing, with limited research on processing techniques. Therefore, the best solution should be found through a combination of Chinese and Western methods, so that blueberry fruit can be used reasonably and fully, reducing the waste of blueberry resources and promoting the development of the blueberry industry.
3. 3 Cosmetics
Due to the high pigment content of blueberries, they have been specifically used to produce pigmented products. These pigmented products can not only be used as natural food coloring, but also have light and heat resistance. At the same time, blueberry fruits contain anthocyanins and phenolic compounds, which have the functions of anti-oxidation, anti-wrinkle, and freckle removal, and can be used in the production of cosmetics. Blueberries are already one of the raw materials for high-end cosmetics made from concentrated extracts of various European fruits.
The anthocyanins in these skin care products protect the skin from ultraviolet rays, prevent wrinkles and blemishes, keep the skin supple and smooth, improve elasticity, reduce skin diseases and ripples, prevent moisture loss, and even eliminate scars, remove stains, and whiten the skin. In addition, blueberry pomace is also rich in anthocyanins, which can be used as a natural anti-aging nutritional supplement[9] , thus giving rise to the new product of a blueberry pomace mask. This not only makes full use of blueberry resources, but also provides a new idea for the development of the blueberry cosmetics industry.

4 Development of the blueberry industry
After more than ten years of development, China has gradually become one of the world's major blueberry producing and consuming regions. The positive development of the blueberry industry in China has attracted many powerful international companies to enter into joint ventures and collaborations with Chinese companies, which has promoted the exchange of technology and the further promotion of mechanization in production. This has reduced the proportion of labor costs in production costs and stimulated the rapid development of the blueberry industry in China.
However, there are still many problems, such as the lack of industry organization coordination and reasonable variety planning; the products and derivatives are relatively monotonous and similar; there is a lack of market demand analysis as most of the focus is on the conventional processing of products; the research and development of new products has not been able to keep up with market demand; the storage and transportation technology for fresh fruit after picking is immature, resulting in serious waste of resources and an increase in labor costs. Blueberries are a labor-intensive industry, especially in terms of harvesting. Affected by the aging population and the loss of rural labor, there is a shortage of human resources during the harvest season, and labor costs are increasing. According to data, in 2019, the labor cost for picking 250 kg of blueberries in Qingdao was about 2 yuan, accounting for 1/4 to 1/3 of the total cost[10] . In the future, it is still necessary to further reduce the production cost of blueberries, such as labor costs, while increasing product development according to market demand and extending the industrial chain, thereby improving industrial efficiency and promoting the healthy and sustainable development of the industry.
References
[1] Yao Jiayu, Li Zhijian. Research progress of blueberry anthocyanins in ophthalmic diseases [J]. International Journal of Ophthalmology, 2016, 16(12): 2234-2236.
[2] Jia Ying, Hu Zhihe. Study on the stability of anthocyanins in blueberry drinks [J]. Nuclear Agricultural Journal, 2016, 30(5): 941-948.
[3] Han Pengxiang, Zhang Bei, Feng Xiqiao, et al. Nutritional and health-promoting functions of blueberries and their development and utilization [J]. Food Industry Technology, 2015, 36 (6): 370-375, 379.
[4] Li Dianxin, Dai Yuanwei, Chen Wei, et al. Research progress on the nutritional value and health-care functions of blueberries [J]. Agricultural Products Processing, 2018(4) :69-70.
[5] Li Bin, Lei Yue, Meng Xianjun, et al. Research progress on the nutritional and health functions of blueberries and the extraction technology of their active ingredients [J]. Food and Machinery. 2015, 31(6): 251-254.
[6] Sun Qianyi, Lu Baojun, Zhang Jing. Research progress of blueberry anthocyanins [J]. Food Industry Science and Technology. 2016, 37(20): 381-384, 390.
[7] Li Sen, Mo Yican. Research overview of blueberry beverages [J]. China Brewing, 2016, 35(7): 11-14.
[8] Feng Guitao, Peng Qianrong, Yang Min, et al. Research progress on the extraction and purification of blueberry anthocyanins and their bioactivities [J]. Chinese Condiments, 2016, 41(4): 146-152.
[9] Cheng Yousheng, Wang Hongfei, Xu Feng, et al. Study on the extraction and oxidation activity of anthocyanins from blueberry pomace [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2015, 32 (4): 696-704.
[10] Zhang Yunwei, Dong Guoqiang, Li Guocheng, et al. Current situation and development strategies of the blueberry industry in Qingdao [J]. Deciduous Fruit Tree. 2018, 50(1): 20-22.
-
Prev
What Are the Uses of Blueberry Fruit in Tamil?
-
Next
Is Blueberry Extract Anthocyanin an Antioxidant?


 English
English French
French Spanish
Spanish Russian
Russian Korean
Korean Japanese
Japanese




