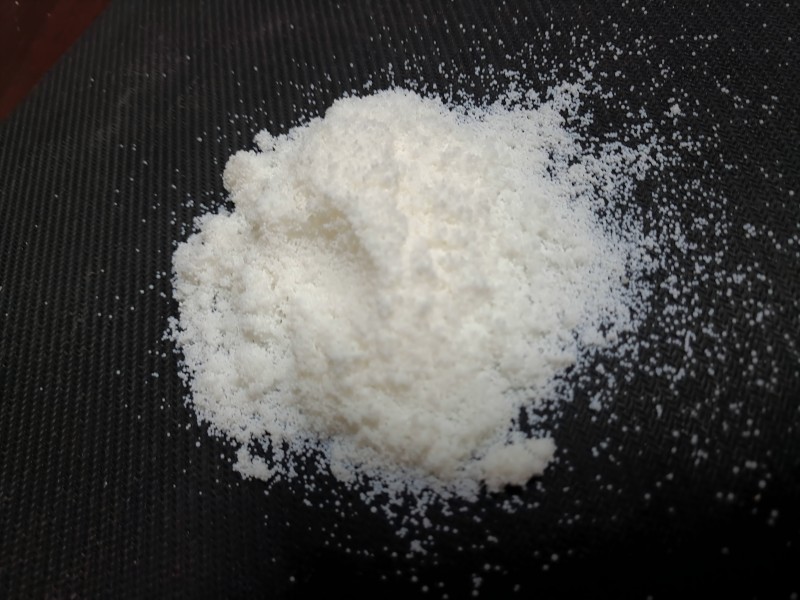
Do You Know A New Process For Efficient Extraction Of High Purity Centella Asiatica Glycosides?
Centella asiatiea (L) Urban is the dried whole herb of Centella asiatiea (L) Urban, family Umbelliferae, which is widely distributed south of the Yangtze River Basin, and the whole herb is used as a medicine, which has been used for thousands of years in the field of medicine in many countries. The chemical constituents in Centella Asiatica include triterpene saponins, triterpene acids, polyynes, and volatile oils [1].

Modern studies have demonstrated that Centella asiatica extract can effectively promote skin damage, local collagen synthesis, and metabolism, and has an important role in tissue repair after skin damage [2]. At the same time, it has inhibited the proliferation of fibroblasts, anti-renal interstitial fibrosis, anti-mammary hyperplasia, anti-tumor, anti-ulcer, anti-depression, and other effects.
According to the investigations conducted by the Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, the Jiangsu Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Botanical Branch of the Shanghai Museum of Nature, and the Hangzhou Botanical Garden of Zhejiang Province, Centella Asiatica is mainly found in Longjin, Xiuoren, Xing'an, Baise, and Damiao Mountains in Guangxi [4].
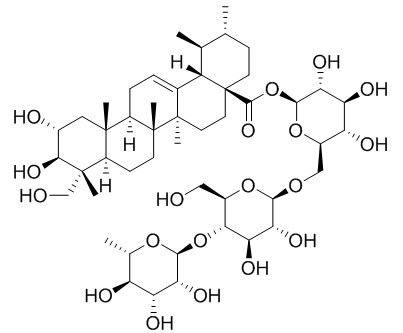
Centella Asiatica extract contains Centella Asiatica glycosides, which can be used to inhibit the formation of surgical and traumatic stigmata, stimulate the growth of granulation, and promote the healing of wounds. It has certain therapeutic effects on patients with venous insufficiency and varicose veins, as well as those who suffer from depression, renal disease, and mammary gland hyperplasia.

The new process of efficiently extracting high purity Centella Asiatica Glycosides is to use the whole herb of Centella Asiatica as the raw material, and after a series of extraction, concentration, purification, decolorization, recrystallization, and other key technical processes, to obtain high purity of Centella Asiatica Glycosides.
1 Technological Principle, Process Flow and Main Technical Indexes
1.1 Technological Principle
Centella Asiatica contains a variety of triterpenoids, including the α-resinol structure. The main components are asiaticoside, hydroxyasiaticoside, Asiatic acid, and hydroxyasiatic acid, which are water-soluble. Cellulase has a biocatalytic effect in accelerating the decomposition of fibers. By adding cellulase and refluxing with heat, the asiaticoside can be well dissolved in the solvent with the aid of active ingredients such as asiatico flavonoids and asiatico polysaccharides.
At this point, the use of two-component clarifier flocculation clarification, removes the solution of tannins, proteins, resins, waxes and other colloidal components, to accelerate the clarification speed, to achieve the purpose of separation. Using the adsorption properties of polystyrene-type large-pore adsorption resin and the purification of molecular sieve, the extract of Centella Asiatica through the appropriate pore size of the resin, which can separate Centella asiatica glycosides and other components of Centella Asiatica, to achieve the purpose of enrichment, purification and decolorization of Centella Asiatica glycosides. At a certain temperature, the solute in the solvent dissolved in the maximum amount will be saturated, and when in a state of supersaturation solution will precipitate crystals.
1.2 Process Flow (As Shown in Figure 1)
(1) Select the whole grass of artificially grown or wild Centella Asiatica, put it in the extraction tank after removing impurities, drying, and crushing, add cellulase into the solution, and heat and reflux extraction several times.
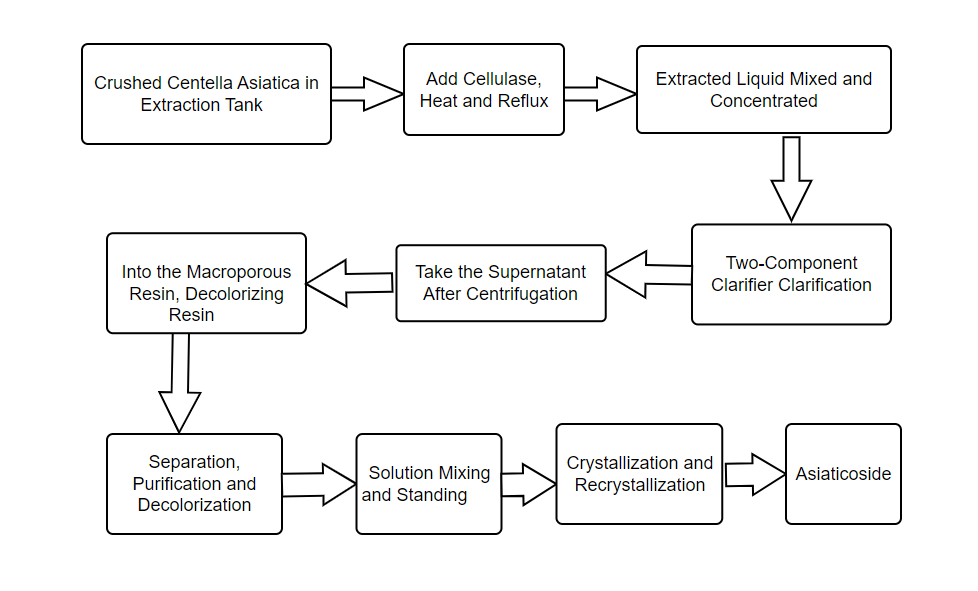
(2) The extract is mixed and concentrated, and the concentrate is clarified with a two-component clarifier and then centrifuged.
(3) The supernatant was purified by chromatography on a macroporous resin column.
(4) The supernatant was decolorized on a decolorizing resin column.
(5) The eluate and effluent were mixed, concentrated, and left for several hours to precipitate crystals, which were then dissolved to saturation by heating with low-carbon alcohol, left to recrystallize.
(6) After drying and crushing, the extract of Centella Asiatica with the main ingredient of Centella Asiatica glucoside (content ≥92%, once crystallized) is produced, and the extraction rate is ≥85%.
1.3 Main technical indicators
The content of Centella Asiatica glucoside produced by this process is ≥95%, and the extraction rate is ≥85%. The main performance indicators are as follows.
(1) Sensory indicators: white powder, with an inherent odor.
(2) Physicochemical index: Asiaticoside ≥95%, weight loss on drying ≤2%, ash ≤1%, total heavy metals ≤20 mgkg, arsenic ≤2.0 mgkg, mercury ≤0.2 mg/kg, lead ≤5.0 mg/kg, cadmium ≤0.3 mg/kg, copper ≤20 mg/kg, aflatoxin B1 ≤5.0 ug/kg.
(3) Pesticide residue index: hexachlorobenzene ≤ 0.1mgkg, DDT ≤ 0.1mg/kg, quintozene ≤ 0.1 mg/kg, aldrin ≤ 0.02 mg/kg.
(4) Microbiological indicators: total number of colonies ≤1000 cfu/g, mold + yeast ≤100 cfu/g, E. coli shall not be detected.
2 Technological Innovations
The Technical Innovation Points of This Process Are as Follows:
(1) Cellulase pretreatment process. Crushed Centella asiatica raw materials are placed in the extraction tank, and cellulase is added into the solution proportionally. Under a certain temperature environment, soak for 1h, then heat to boiling for extraction. For the second extraction, add appropriate water proportionally, soak for 2h, and then extract again. Cellulase hydrolysis, destruction of cell walls, increase cell membrane permeability so that the target components are more easily dissolved and analyzed; Centella Asiatica glycosides in the Centella Asiatica flavonoids, Centella Asiatica polysaccharides and other components of the solubilization can be well dissolved in water.
Compared with the traditional alcohol extraction process, the new process has the advantages of good extraction effect, low production costs, a wide range of materials, conducive to industrial production; compared with the traditional water extraction process, the new process has the advantages of fast extraction speed, extraction is more complete, high extraction rate.
(2) Concentrate clarifier treatment process. Add ZTC two-component clarifier into the concentrate according to a certain ratio of material and concentrate, and use it to remove colloidal components such as tannin, protein, resin, and wax. The use of clarifying agent can speed up the clarification speed, but also can preserve the target components; can effectively solve the solution after centrifugation, the color turbidity problem, but it also not easy to block the macroporous adsorption resin.
The application of a two-component clarifying agent makes the process simpler, easier to clarify the solution, more efficient extraction, lower cost, and shorter process.
ZTC two-component clarifying agent consists of two kinds of components, one group plays the role of the main flocculation, and the other group plays the role of auxiliary flocculation, which greatly accelerates the clarification process, which is 3~5 times faster than the traditional clarifying agent.
(3) Decolorizing resin decolorizing process. The eluent is decolorized by polystyrene-type macroporous decolorizing resin (eluted with several times of the column volume of water). Compared with the traditional alumina resin column, this resin has good effect of removing pigment, strong specificity, convenient regeneration, and can be reused for many times.
The core technology of the new process for the efficient extraction of high purity centella asiatica glycosides has been granted a national patent [5].

3 Key Technologies and Processes
The key technology and process technology design of this project is based on the physical and chemical properties of Centella Asiatica glucoside as the basic basis, in the process mainly solved the following key technologies.
(1) Determine the proportion of cellulase and raw materials, raw materials, and water, to determine the number of extractions, extraction time, and extraction temperature.
The main components of Centella Asiatica are asiaticoside, hydroxyasiaticoside, asiatic acid, and hydroxyasiatic acid, which are soluble in water. Cellulase in the decomposition of fiber, plays a role in accelerating the decomposition, in the Centella Asiatica flavonoids, Centella Asiatica polysaccharides and other active ingredients of solubility, Centella Asiatica glycosides can be well dissolved in the solvent.
(2) Screening a better two-component clarifying agent. Utilizing the flocculation and clarification effect of two-component clarifying agent, removes tannins, proteins, resins, waxes, and other colloidal components in the solution, accelerates the clarification speed, and achieves the purpose of rapid separation.
(3) Screening the suitable type of macroporous resin. Using the adsorption property of polystyrene type macroporous adsorbent resin and the purification effect of a molecular sieve, the extract of Centella Asiatica can be separated from other components of Centella Asiatica by passing through the resin with suitable pore size, to achieve the purpose of enrichment, purification, and decolorization of Centella Asiatica glycosides.
The concentration, volume, elution time, temperature range, and decolorization method of the eluent were determined by the suitable eluent type.

4 Conclusion
The high purity asiaticoside extraction technology adopts cellulase pretreatment, heating reflux extraction, two-component concentration and clarification agent treatment, separation and purification by macroporous resin column chromatography, decolorization by decolorizing resin, and saturated precipitation and heat recrystallization to improve the purity of asiaticoside, to make the content of asiaticoside in the extract reach more than 95%.
Compared with the existing technology, the new process has the advantages of simple process flow, short production cycle, low organic solvent consumption, low production cost, suitability for mass production, and so on.
References
[1] GB/T 50328-2001, Specification for filing and organizing construction project documents [s].
[2] Lv Luo, Wei Shaomin, Lin Huifen, et al. Effect of Centella asiatica extract on collagen synthesis in fibroblasts[J]. Daily Chemical Industry, 2002,32(6):23-25.
[3] Dai Baidong, Zhang Cui, Wang Jia, et al. Research status of Centella asiatica[J]. Shanghai Medicine, 2008,29(2):89-90.
[4] ZHANG Li, KE Zheng, XIONG Xiaojun. Resource distribution, chemical composition and pharmacological activity of Centella Asiatica [A]. Proceedings of the National Symposium on Biochemical and Biotechnological Drugs [C].2003.
[5] Lu Zhaokai, Lu Qiaonian. A kind of Centella Asiatica glucoside and its preparation method [P]. China Patent: ZL200810303151.9,2008-07-29.


 English
English French
French Spanish
Spanish Russian
Russian Korean
Korean Japanese
Japanese







