Botanical Extracts for Cosmetics Sunscreen: A Natural Way to Protect Your Skin
FDA-approved organic sunscreens include p-aminobenzoic acid, dibenzoylmethane, and dibenzone-3 [1]. The common feature of the molecular structure of these sunscreens is that they all contain a benzene ring or conjugated structure, which has a good absorption of UV light. In plants, secondary metabolites such as flavonoids, phenylpropanoids, polyphenols, and carotenoids also have benzene rings or conjugated structures. Therefore, they also have significant UV absorption properties and are considered natural sunscreens. Meanwhile, the sunscreen efficacy components in botanical extracts for cosmetics also have a protective effect on UV-induced sunburn and photoaging of the skin [2]. People prefer botanical extracts for cosmetics sunscreen since it is a natural way to protect the skin. Below are some botanical extract ingredients for cosmetics sunscreen that have been proven efficient.

1. Flavonoids
Flavonoids are widely found in various plants. Their structure is characterized by 2 benzene rings, and most of them have conjugated structures. Flavonoids can absorb ultraviolet rays with a wavelength of 200~400 nm, especially UVA and UVB. flavonoids added to sunscreen cosmetics not only absorb ultraviolet rays but also have the effect of anti-photo-aging and regulating the signaling pathway of sunburn. Anthocyanins belong to a special class of flavonoids, which are water-soluble natural pigments widely found in plants. Most flowers and fruits, such as roses, safflower, grapes, cranberries, and mulberries, are variously colored due to anthocyanins. The presence of phenolic hydroxyl groups and a high degree of cross-conjugation system in anthocyanins gives them strong absorption in both the ultraviolet and visible regions.
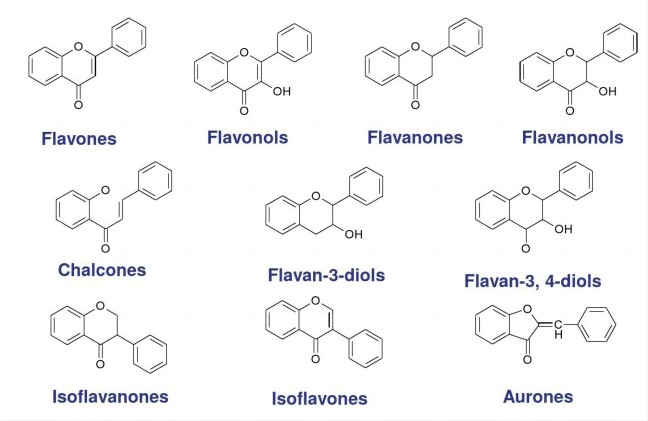
Rutin and quercetin are the most common and widely studied flavonoids in plants. Rutin and quercetin have maximum absorption peaks at 373 and 341 nm, respectively. The combination of rutin or quercetin with titanium dioxide and zinc oxide has a synergistic sunscreen effect, respectively. The synergistic effect of rutin and benzophenone also increased the original sun protection index (SPF). Also, rutin and quercetin are good antioxidants [3].

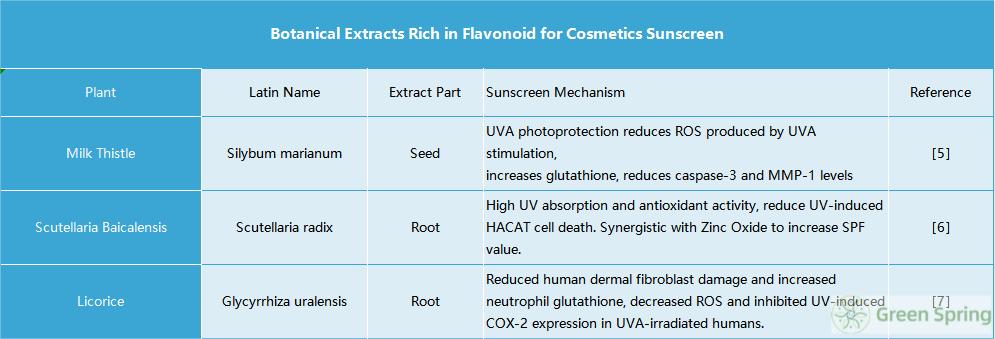
Many plants are rich in flavonoids, such as ginkgo biloba, Sophora japonica, Milk Thistle, Scutellaria baicalensis, licorice, and Puerariae. Ginkgo biloba extract is rich in flavonoids such as rutin and quercetin. Ginkgo biloba extract formula can protect skin barrier function from damage caused by ultraviolet radiation. The combination of ginkgo biloba extract and green tea extract improved the barrier damage, erythema, and sunburn cells caused by ultraviolet radiation on the skin. Meanwhile, both extracts have strong free radical scavenging activity and are widely used in natural products with antioxidant properties [4]. Extracts from Silybum marianum [5], Scutellaria radix [6], and Glycyrrhiza uralensis [7] not only have sunscreen effects but also have good post-sun repair and antioxidant effects, thereby protecting the skin from UV damage and they have been adopted for cosmetics sunscreen.
2. Phenylpropanoid
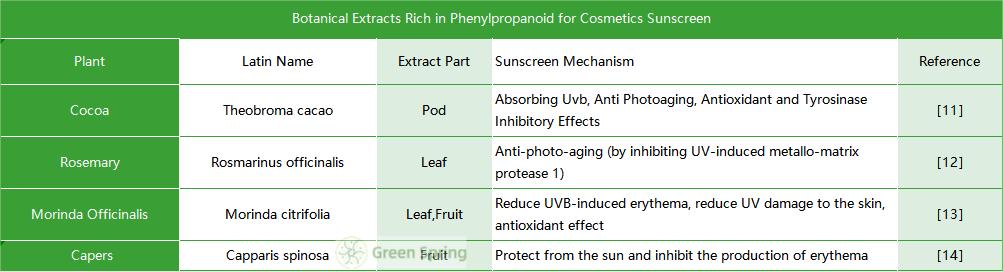
The main phenylpropanoid compounds in plants are ferulic acid, cinnamic acid, caffeic acid, rosemarinic acid, chlorogenic acid, tanshin, and rhodioloside. Most phenylpropanoid compounds have phenolic hydroxyl groups in their molecular structure, making them highly absorbent of ultraviolet light. Since the structure of phenylpropanoid is similar to tyrosine, small molecules of phenylpropanoid analogs also have a good effect of inhibiting tyrosinase activity.
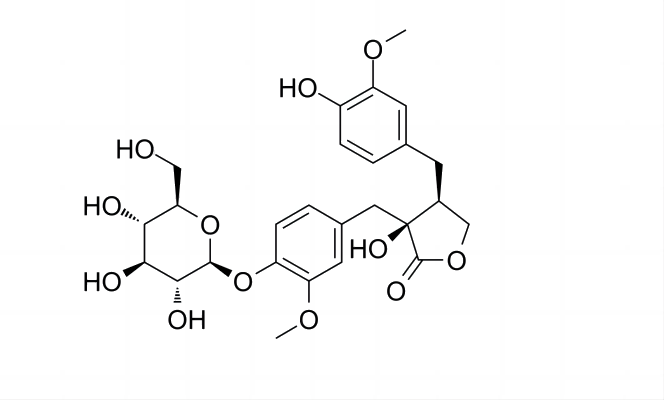
Rhodioloside is the main active ingredient of Rhodiola rosea extract, which has a good antioxidant effect and inhibits tyrosinase activity, as well as protects against UVB-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis, and also attenuates UV-induced skin inflammation by targeting cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), and is non-toxic to the cells [8]. Ferulic acid is a sunscreen as well as an antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibitor and is found in high concentrations in Chinese herbs such as Angelica sinensis and Rhizoma Ligustici Chuanxiong, and in raw materials such as coffee and cereal hulls. Ferulic acid reduces UVB-induced lipid peroxidation in human lymphocytes and inhibits UVB-induced production of e.g. glutathione peroxidase and oxidized glutathione [9]. Ferulic acid has been compounded with some sunscreens to enhance both SPF and UVA-PF values as well as safety [10].

3. Polyphenols
Plant polyphenols are also widely found in the skin, roots, leaves and fruits of plants. Broadly speaking, plant polyphenols include not only tannins or ellagitannins, but also a variety of small molecule phenolic compounds in plants, such as Catechol, Salvianolic acid, gallic acid and ellagic acid, etc. Because of their polyphenolic structure, plant polyphenols have good UV absorption. Because of their polyphenolic structure, plant polyphenols have excellent UV absorption.
Epigallocatechin, also known as epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), is the main polyphenol component of green tea extract. EGCG reduces UVB-induced erythema, decreases UVB-induced ROS production by human skin leukocytes, protects the skin from UV-induced immunosuppression, and prevents inflammatory skin diseases, photoaging, and photocarcinogenesis [15]. Green tea extract sunscreen has the ability to reduce photoaging, reduce UVB-induced carcinogenesis and inflammatory response, reduce UVB-induced inflammatory leukocyte infiltration and peroxidase activity in the skin, and inhibit UVB-induced protein oxidation and DNA damage thereby reducing skin photodamage. Green tea extract not only reduces UVB-induced carcinogenesis and inflammation but also has a high protective effect against UV radiation-induced oxidative stress in the skin [16].
Grape seed extract contains polyphenolic compounds such as EGCG, proanthocyanidins, catechins, epicatechins and gallic acid, which have excellent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. The addition of sunscreen cosmetics helps to reduce the amount of other sunscreens added and reduces the potential risk of sunscreens [17]. In addition, grape seed extract shows very high photostability to some sunscreens, increasing the broad spectrum of UV absorption and thus enhancing photoprotection. In addition, resveratrol in grape seed extract significantly inhibited UVB radiation-induced skin edema and inflammation, hydrogen peroxide production and lipid peroxidation in the skin [18]. It has been used as an excellent botanical extract for cosmetics sunscreen.

4. Carotenoids
Carotenoids, mainly lycopene, astaxanthin, lutein and β-carotene, are fat-soluble pigments found widely in plants. As potential photoprotectants, carotenoids have excellent antioxidant activity, preventing oxidation by free radicals attacking different molecules, including molecules in skin tissues. Single-linear oxygen radicals are the most dangerous reactive oxygen species produced in the skin after sunlight exposure; lycopene has a very good antioxidant effect against single-linear oxygen radicals. Astaxanthin has a strong absorption peak at 478 nm, and has a good scavenging ability for DPPH radicals, and is also a good natural antioxidant.

Astaxanthin interferes with UVA-induced MMP-1, and its topical application and/or oral administration can prevent and/or reduce UVA-associated photoaging features such as skin laxity and/or wrinkles [24]. Lutein reduces photoaging induced by UVB irradiation and contributes to the protection of the skin from UV irradiation-induced damage, and also reduces free radical damage to keratinocytes through antioxidant activity [25]. West Indian cherry (Malpighia glabra) extract is rich in carotenoids and sunscreens made from its extracts have good UVB absorption, when compounded with organic sunscreens, they synergistically protect the skin from UV radiation damage and also have antioxidant activity.

5. Other
Some other types of compounds in botanical extracts have also been shown to have a good sunscreen effect. The main component of ginseng (Panax ginseng) extract is ginsenoside, a triterpenoid saponin. Ginseng extract has been shown to significantly reduce UV-induced skin wrinkles, attenuate epidermal hyperplasia, and increase dermal cell density, as well as have anti-inflammatory and photoprotective effects [26]. The fruits and seeds of many plants are rich in unsaturated fatty acids, which have some SPF and sunscreen properties, and also serve as base oils in cosmetic formulations [27]. For example, the W/O sunscreen compounded with coffee oil and sunscreen increased SPF and had no cytotoxic effect [28].

The sunscreen efficacy components of plants not only have the UV absorption effect of sunscreen, but also have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory or preventive repair effects. Therefore, the research and development of botanical extracts in sunscreen cosmetics application is an inevitable trend.
However, the content of sunscreen ingredients in such plant crude extracts is usually low, so that the sunscreen prepared with plant crude extracts does not have a very high sunscreen index. The solubility of plant extracts rich in active ingredients is usually poor, and the compounding is not good, which increases the difficulty of compounding and the skin feel. In addition, due to the prevalence of phenolic hydroxyl groups and cross-conjugated structures in these sunscreen ingredients, these extracts have a variety of colors. These colored plant extracts can only be added in very small amounts to white creams, thus affecting their sunscreen effect. In addition, the phenolic hydroxyl groups and conjugated structures in these colored extracts are easily oxidized, resulting in poor stability. How to solve the refining, stability, solubility and compounding of Sunscreen Ingredients in Botanical Extracts are the difficulties in their application.
Reference:
[1]MohiuddinA K. An Extensive Review of Sunscreen and Suntan Preparations[J]. American Journal of Dermatological Research and Reviews, 2019, 8(1): 1-25.
[2]CefaliL C, AtaideJA,Moriel P, et al. Plant‐based Active Photoprotectants for Sunscreens[J] . International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 2016, 38(4): 346-356.
[3]Benjamin C, Cline C, Eve P, et al. Quercetin and Rutin as Potential Sunscreen Agents: Determination of Efficacy by an in Vitro Method[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2008, 71(6): 1117-1118.
[4]Dal S B, Gaspar L R, Maia P C. Photoprotective Effects of Topical Formulations Containing a Combination of Ginkgo Biloba and Green Tea Extracts[J]. Phytotherapy Research: PTR, 2011, 25(12):1854-1860.
[5]SvobodovA R, GabrielovE, Michaelides L, et al. UVA-Photoprotective Potential of Silymarin and Silybin[J]. Archives of Dermatological Research, 2018, 310(5): 413-424.
[6]Seok J K, Kwak J Y, Choi G W, et al. Scutellaria Radix Extract as a Natural Uv Protectant for Human Skin[J]. Phytotherapy Research, 2016, 30(3): 374-379.
[7]Ry S N, Jong-Eun K, Seong P J, et al. Licochalcone A, A Polyphenol Present in Licorice, Suppresses UV-induced COX-2 Expression by Targeting PI3K, MEK1, and B-Raf[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2015, 16(3): 4453-4470.
[8]Wu D, Yuan P, Ke C, et al. SalidrosideSuppresses Solar Ultraviolet-Induced Skin Inflammation by Targeting Cyclooxygenase-2[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(18): 25971-25982.
[9]Rajendra N, Ramachandran S, Kodukkur V, et al. Ferulic Acid Inhibits Uv-B–induced Oxidative Stress in Human Lymphocytes[J]. Nutrition Research, 2007, 27(9): 559-564.
[10]Anbanandam Parthiban A V. Biorenewable Functional Oligomers and Polymers - Direct Copolymerization Offerulic Acid to Obtain Polymeric UV Absorbers and Multifunctional Materials[J]. Polymer, 2020, 188(1): 1-10.
[11] Karim A A, Azlan A, Ismail A, et al. Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant,Anti-Wrinkles and Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activities of Cocoa Pod Extract[J]. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2014, 14(1): 381.
[12]Liu Li, Zhen Yaxian. Water-Soluble Rosemary Extract Achieves Photoprotective Effect by Inhibiting Uv-Induced Metalloproteinase-1[J]. Chinese Journal of Dermatology, 2009, 42(7): 535.
[13]West B J, Deng S, Palu A K, et al. Morinda citrifolia Linn. (Rubiaceae)Leaf Extracts Mitigate Uvb-Induced Erythema[J]. Journal of Natural Medicines, 2009, 63(3): 351-354.
[14]Bonina F, Puglia C, Ventura D, et al. In Vitro Antioxidant and in Vivo Photoprotective Effects of a Lyophilized Extract of Capparis Spinosa L. buds[J]. Journal of Cosmetic Science, 2002, 53(6): 321-336.
[15]Katiyar S K, Matsui M S, Elmets C A, et al. Polyphenolic Antioxidant Epigallocatechin‐3‐gallate from Green Tea Reduces UVB‐Induced Inflammatory Responses and Infiltration of Leukocytes in Human Skin[J]. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 1999, 69(2): 148-153.
[16]Nichols J A, Katiyar S K.Skin Photoprotection by Natural Polyphenols: Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant And DNA Repair Mechanisms[J]. Archives of Dermatological Research, 2010, 302(2): 71-83.
[17]Martincigh B S, Ollengo M A. The Photostabilizing Effect of Grape Seed Extract on Three Common Sunscreen Absorbers[J]. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2016, 92(6): 870-884.
[18]Afaq F, Adhami V M, Ahmad N. Prevention of Short-Term Ultraviolet B Radiation-Mediated Damages by Resveratrolin SKH-1 Hairless Mice [J] . Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2003, 186(1): 28-37.
[19]Figueiredo S A, Vilela F M, Da Silva C A, et al. In Vitro and in Vivo Photoprotective/Photochemopreventive Potential of Garcinia Brasiliensis Epicarp Extract[J] . Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2014, 13(1): 65-73.
[20]VebericR, JakopicJ, Stampar F, et al. European elderberry(Sambucus nigra L.)Rich in Sugars, Organic Acids, Anthocyanins and Selected Polyphenols[J]. Food Chemistry, 2009, 114(2): 511-555.
[21]Sachdeva M, Katyal T. Abatement of Detrimental Effects of Photoaging by Prunus Amygdalus Skin Extract[J]. International Journal of Herbal Medicine, 2011, 5(2): 12-15.
[22]Hwang I, Yoo K-Y, Kim D, et al. An Extract of Polygonum Multiflorum Protects Against Free Radical Damage Induced by Ultraviolet B Irradiation of the Skin[J]. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 2006, 39(9): 1181-1188.
[23]Jang S, Chun J, Shin E M, et al. Inhibitory Effects of Curcuminoids from Curcuma Longa on Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 Expression in Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation, 2012, 42(1): 33-39.
[24]Genji I. The Xanthophyll Carotenoid Astaxanthin Has Distinct Biological Effects to Prevent the Photoaging of the Skin Even by Its Postirradiation Treatment[J]. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2019, 95(2): 490-500.
[25]Sutatip P, Prateep W, Ongart L, et al. Protective Effect of Silk Lutein on Ultraviolet B-Irradiated Human Keratinocytes[J]. Biological Research, 2013, 46(1): 39-45.
[26]Lee H, Lee J Y, Song K C, et al. Protective Effect of Processed Panax Ginseng, Sun Ginseng on Uvb-Irradiated Human Skin Keratinocyte and Human Dermal Fibroblast[J]. Journal of Ginseng Research, 2012, 36(1): 68.
[27]Marto J, Gouveia L F, Chiari B G, et al. The Green Generation of Sunscreens: Using Coffee Industrial Sub-Products[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2016, 80(1): 93-100.
[28]Chiari B G, Trovatti E, Pecoraro É, et al.Synergistic Effect of Green Coffee Oil and Synthetic Sunscreen for Health Care Application[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2014, 52(3): 89-93.
-
Prev
5 Amazing Ingredients of Botanical Extracts for Cosmetics Moisturizing
-
Next
The 5 Most Successful Botanical Extracts For Hair Examples


 English
English French
French Spanish
Spanish Russian
Russian Korean
Korean Japanese
Japanese



