A Beginner's Guide to Rice Bran Wax Composition
With the development of the rice bran oil production industry, brings a large amount of by-product rice bran wax. Rice bran wax is an important natural wax resource. Regarding rice bran wax composition, some people began to explore it as early as more than fifty years ago, and in the early years, there were Winkag, Nabenmuller and Anderson, Tanshita, Yamazaki and Ogawa, Ueno, Tsuchiya, Janei, Mikado, etc., and in recent years, there were Iwama and Maruta, Takagi, Iwata, etc. With the development of chromatography technology after the 60's, with the advancement of analytical methods and techniques, rice bran wax composition so far has been basically clarified.[1]Below is a beginner's guide to rice bran wax composition.

Unlike Brazilian carnauba wax and beeswax which contain diesters, triesters, diol esters, etc., the composition of rice bran wax is relatively simple, most of which are wax esters composed of diphasic long-chain fatty acids and diphasic long-chain aliphatic mono-tertiary alcohols, and other components are very few [2][3], this paper analyzes the common physicochemical constants and the compositions of rice bran waxes from different sources and different degrees of refinement.

1 Experiments and Methods
1.1 Raw material
Refined rice bran wax samples were taken from Zhejiang Grain Research Institute, Japan House General Corporation, Zhejiang Huzhou Cereal and Oil Steaming Plant, Hunan Changsha Oil Chemical Plant and homemade; crude rice bran wax was taken from Zhejiang Huzhou Cereal and Oil Steaming Plant.
1.2 Physical and Chemical Constants
Melting point, acid value, saponification value, iodine value are shown in the experimental handout of oil and grease chemistry of Wuxi University of Light Industry.
1.3 Composition
1.3.1 Hydrolysis: weigh rice bran wax 2g add 3 times water, heat to 85℃, wait for complete melting under stirring, add NaOH water solution, super alkali amount 1 time, boil 8h~12h, keep warm for 36h, add and saponify with alkali equivalent amount of saturated aqueous solution of calcium chloride, react around 80℃ for 2h~3h, wash with hot water to neutral, dry, get grayish-white powder particles that are a fatty alcohol and fatty acid calcium Mixture of fatty alcohol and calcium fatty acid.
1.3.2 Fatty alcohol production: gray-white particles into the Soxhlet extractor, with 6-8 times the acetone extraction at 16h, the extract is placed at room temperature to precipitate crystals, and filtration to get fatty alcohol.

1.3.3 Fatty acid production: extract the residual powdered calcium fatty acids, add 4 times the water stirring, heating 70 ℃ ~ 80 ℃, slowly add concentrated hydrochloric acid, adjust the pH to 1 ~ 2, boiling 3h, until the disappearance of solid particles, cooling, hot water wash the upper layer of solids to neutral, to get fatty acids.
1.3.4 Acetylation of fatty alcohols: Weigh 0.2g of sample, add 3ml of acetylation (1 part of acetic anhydride and 3 parts of pyridine mixed) reagent, heating and mixing, reflux for 1h, add 40ml of benzene, washed with water, the benzene layer is dried and dehydrated with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtration, concentration, and used as a gas chromatography analysis.
1.3.5 Methyl esterification of fatty acids: Methyl esterification by acid contact method, see Wuxi Light Industry University Oleochemistry Laboratory Handout.
1.3.6 Gas chromatography analysis: Sigma115 gas chromatograph (PE company), 12m × 0.32mm capillary column, fixed liquid OV-101, FID detector, column temperature 180℃ ~ 300℃, carrier gas N2, line speed 20cm/s, temperature increase rate 5℃/min, detector temperature 300℃, sample temperature 320℃. 320℃.
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Physicochemical constants of rice bran waxes
Table 1: Physicochemical Property Constants of Rice Bran Wax Samples
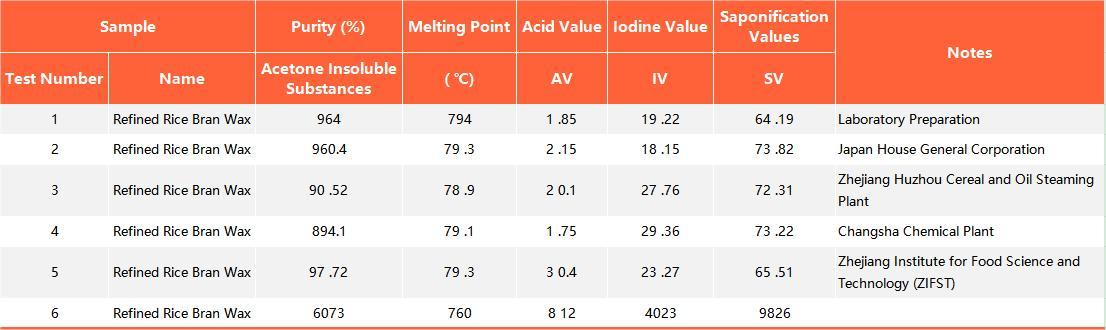
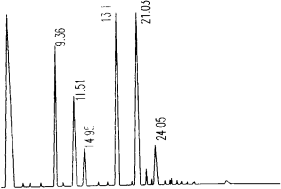
Figure 1: Gas Chromatography of Fatty Alcohols in Rice Bran Wax
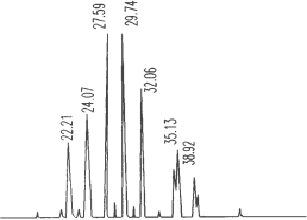
Table 2: Fatty Alcohol Composition of Rice Bran Wax (%)
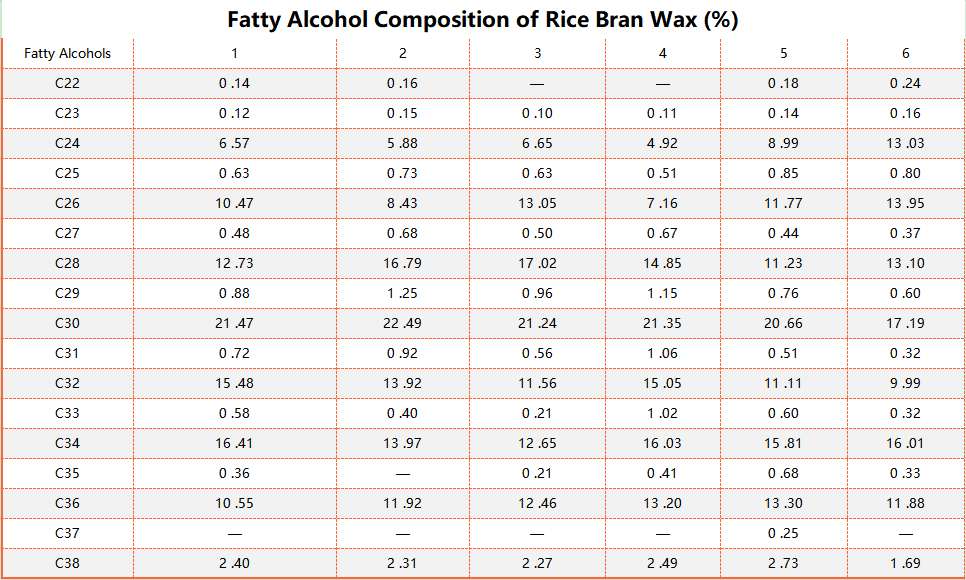
Table 3: Fatty Acid Composition of Rice Bran Wax (%)
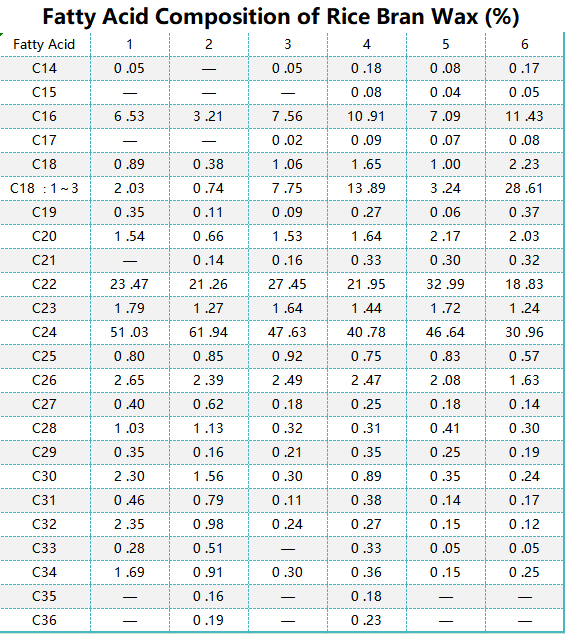
Table 1 (Physicochemical property constants of rice bran wax samples) shows the physicochemical property constants of six samples. It can be seen that the saponification method resulted in the lowest purity of the refined waxes. The waxes refined in this experiment were in a better position compared to the other samples in terms of all indices.
2.2 Compositional Analysis
2.2.1 Fatty alcohol composition of rice bran wax
Fig.1 is the gas chromatogram of fatty alcohol in rice bran wax, and the standard C18 fatty alcohol is used for characterization, then Other peaks are characterized according to the relative retention index, and the content of each component is calculated by peak area normalization method. Table 2 shows the composition of fatty alcohols in six waxes, from which it can be seen that the carbon number distribution ranges from C22 to C38, the even-carbon alcohols accounted for about 95%, and the fatty alcohols above C30 accounted for about 60%, among which the content of C30 fatty alcohols was the largest.
2.2.2 Fatty Acid Composition of Rice Bran Wax
Figure 2 shows the gas chromatograms of fatty acids in furfury wax. The qualitative and quantitative methods were the same as those of fatty alcohols, and the qualitative standard was stearic acid. Table 3 shows the fatty acid composition of 6 kinds of wax samples. From Table 3, it can be seen that the carbon number of fatty acids in furfury wax ranges from C14 to C36, which is much longer than that of the fatty acid carbon chain of the general animal and plant fats and oils, and even carbon number accounts for about 95%, and the fatty acids of C22 and C24 are the main ones, and the total of both of them accounts for about 60%, and they also contain unsaturated fatty acids, and they are dominated by mono olefins, diolefins and triolefins in C18, and the content of them decreases with the degree of refinement of waxes. The content decreases as the degree of wax refining increases. In the crude wax, the content of C18:1-3 reaches 28.61%, which is mainly due to the high oil content in the crude wax and the high content of oleic acid and linoleic acid in the rice bran oil.
2.2.3 Composition of Rice Bran Wax
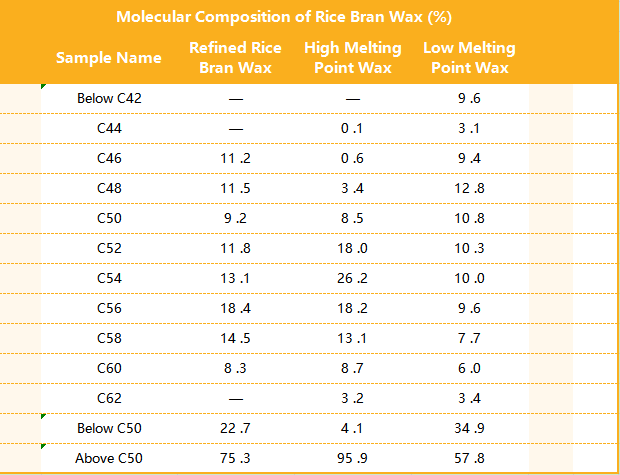
Rice bran wax is mainly composed of wax esters consisting of even-carbon long-chain fatty acids and even-carbon long-chain aliphatic monohydric alcohols. It is reported that the total length of its carbon chain is C44~C62, and Table 4 shows the carbon chain distribution of different wax samples. Table 4 shows the distribution of carbon chains of different waxes. It can be seen from Table 4 that the wax esters with carbon chain lengths of C50 and above are the main wax esters.
3. Conclusion
The rice bran wax composition is like this: the carbon number distribution range of fatty alcohol in rice bran wax is C22~C38, even carbon alcohol accounts for about 95%, and the content of thirty alcohol is the highest. Fatty acid carbon number distribution range is C14~C36, even carbonic acid accounts for about 95%, and C24 acid content is the highest, accounting for more than 40%.
Reference:
[1] Nabenhanar,J.of Chromatography ,1985,305:234,
[2] Yoon, S. H. J. A M. Oil .Chem. Soci., 1982, 59(12):561 3 T Ulloch, A. P., Cosmetics and Perf Umer , 1979, 89:53 4 Toru Takagi . Oleochemistry, 1978, 27(3):172-176
[3] Fumio Iwama .Kigy O K Agaku Zasshi, 1969, 72(12):2605


 English
English French
French Spanish
Spanish Russian
Russian Korean
Korean Japanese
Japanese






